Feed aggregator
In AI We Trust? Increasing AI Adoption in AppSec Despite Limited Oversight
ShinyHunters Wage Broad Corporate Extortion Spree
A cybercriminal group that used voice phishing attacks to siphon more than a billion records from Salesforce customers earlier this year has launched a website that threatens to publish data stolen from dozens of Fortune 500 firms if they refuse to pay a ransom. The group also claimed responsibility for a recent breach involving Discord user data, and for stealing terabytes of sensitive files from thousands of customers of the enterprise software maker Red Hat.
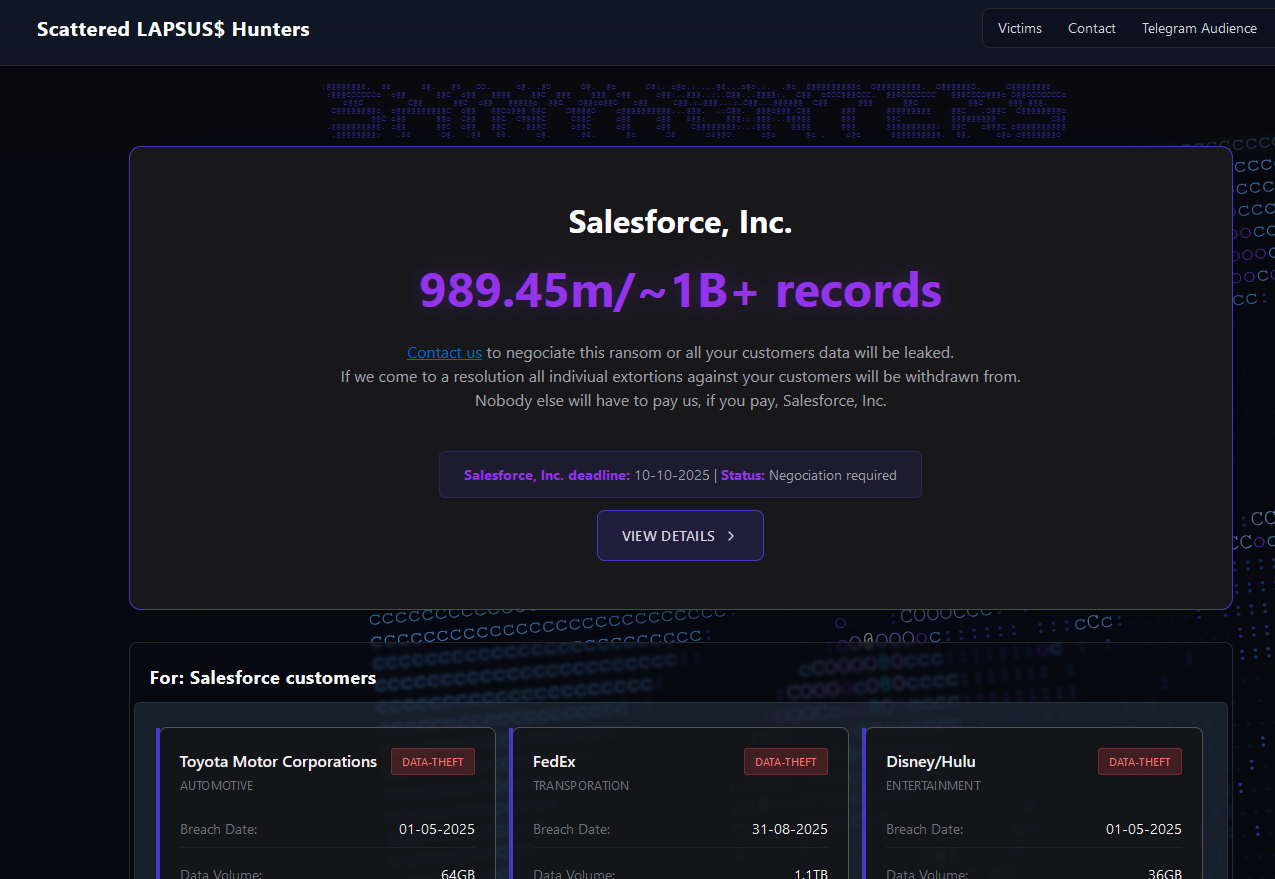
The new extortion website tied to ShinyHunters (UNC6040), which threatens to publish stolen data unless Salesforce or individual victim companies agree to pay a ransom.
In May 2025, a prolific and amorphous English-speaking cybercrime group known as ShinyHunters launched a social engineering campaign that used voice phishing to trick targets into connecting a malicious app to their organization’s Salesforce portal.
The first real details about the incident came in early June, when the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) warned that ShinyHunters — tracked by Google as UNC6040 — was extorting victims over their stolen Salesforce data, and that the group was poised to launch a data leak site to publicly shame victim companies into paying a ransom to keep their records private. A month later, Google acknowledged that one of its own corporate Salesforce instances was impacted in the voice phishing campaign.
Last week, a new victim shaming blog dubbed “Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters” began publishing the names of companies that had customer Salesforce data stolen as a result of the May voice phishing campaign.
“Contact us to negotiate this ransom or all your customers data will be leaked,” the website stated in a message to Salesforce. “If we come to a resolution all individual extortions against your customers will be withdrawn from. Nobody else will have to pay us, if you pay, Salesforce, Inc.”
Below that message were more than three dozen entries for companies that allegedly had Salesforce data stolen, including Toyota, FedEx, Disney/Hulu, and UPS. The entries for each company specified the volume of stolen data available, as well as the date that the information was retrieved (the stated breach dates range between May and September 2025).
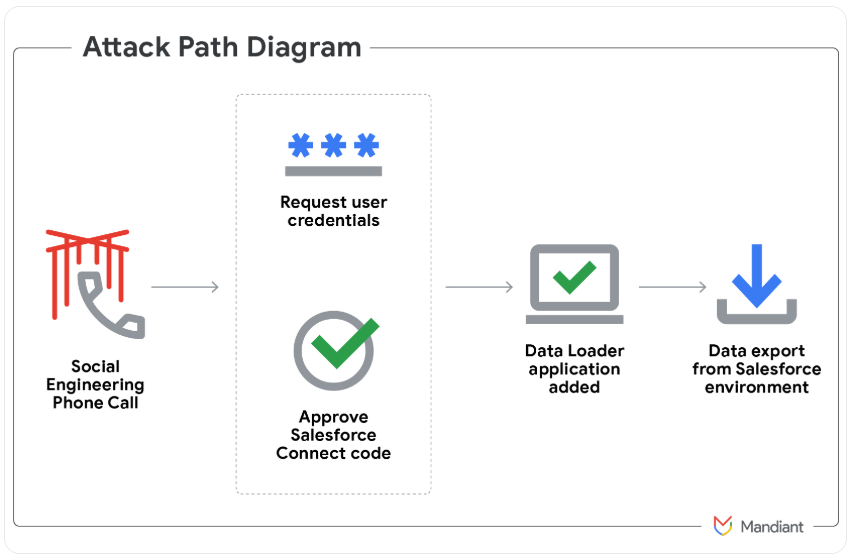
Image: Mandiant.
On October 5, the Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters victim shaming and extortion blog announced that the group was responsible for a breach in September involving a GitLab server used by Red Hat that contained more than 28,000 Git code repositories, including more than 5,000 Customer Engagement Reports (CERs).
“Alot of folders have their client’s secrets such as artifactory access tokens, git tokens, azure, docker (redhat docker, azure containers, dockerhub), their client’s infrastructure details in the CERs like the audits that were done for them, and a whole LOT more, etc.,” the hackers claimed.
Their claims came several days after a previously unknown hacker group calling itself the Crimson Collective took credit for the Red Hat intrusion on Telegram.
Red Hat disclosed on October 2 that attackers had compromised a company GitLab server, and said it was in the process of notifying affected customers.
“The compromised GitLab instance housed consulting engagement data, which may include, for example, Red Hat’s project specifications, example code snippets, internal communications about consulting services, and limited forms of business contact information,” Red Hat wrote.
Separately, Discord has started emailing users affected by another breach claimed by ShinyHunters. Discord said an incident on September 20 at a “third-party customer service provider” impacted a “limited number of users” who communicated with Discord customer support or Trust & Safety teams. The information included Discord usernames, emails, IP address, the last four digits of any stored payment cards, and government ID images submitted during age verification appeals.
The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters claim they will publish data stolen from Salesforce and its customers if ransom demands aren’t paid by October 10. The group also claims it will soon begin extorting hundreds more organizations that lost data in August after a cybercrime group stole vast amounts of authentication tokens from Salesloft, whose AI chatbot is used by many corporate websites to convert customer interaction into Salesforce leads.
In a communication sent to customers today, Salesforce emphasized that the theft of any third-party Salesloft data allegedly stolen by ShinyHunters did not originate from a vulnerability within the core Salesforce platform. The company also stressed that it has no plans to meet any extortion demands.
“Salesforce will not engage, negotiate with, or pay any extortion demand,” the message to customers read. “Our focus is, and remains, on defending our environment, conducting thorough forensic analysis, supporting our customers, and working with law enforcement and regulatory authorities.”
The GTIG tracked the group behind the Salesloft data thefts as UNC6395, and says the group has been observed harvesting the data for authentication tokens tied to a range of cloud services like Snowflake and Amazon’s AWS.
Google catalogs Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters by so many UNC names (throw in UNC6240 for good measure) because it is thought to be an amalgamation of three hacking groups — Scattered Spider, Lapsus$ and ShinyHunters. The members of these groups hail from many of the same chat channels on the Com, a mostly English-language cybercriminal community that operates across an ocean of Telegram and Discord servers.
The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters darknet blog is currently offline. The outage appears to have coincided with the disappearance of the group’s new clearnet blog — breachforums[.]hn — which vanished after shifting its Domain Name Service (DNS) servers from DDoS-Guard to Cloudflare.
But before it died, the websites disclosed that hackers were exploiting a critical zero-day vulnerability in Oracle’s E-Business Suite software. Oracle has since confirmed that a security flaw tracked as CVE-2025-61882 allows attackers to perform unauthenticated remote code execution, and is urging customers to apply an emergency update to address the weakness.
Mandiant’s Charles Carmichael shared on LinkedIn that CVE-2025-61882 was initially exploited in August 2025 by the Clop ransomware gang to steal data from Oracle E-Business Suite servers. Bleeping Computer writes that news of the Oracle zero-day first surfaced on the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters blog, which published a pair of scripts that were used to exploit vulnerable Oracle E-Business Suite instances.
On Monday evening, KrebsOnSecurity received a malware-laced message from a reader that threatened physical violence unless their unstated demands were met. The missive, titled “Shiny hunters,” contained the hashtag $LAPSU$$SCATEREDHUNTER, and urged me to visit a page on limewire[.]com to view their demands.
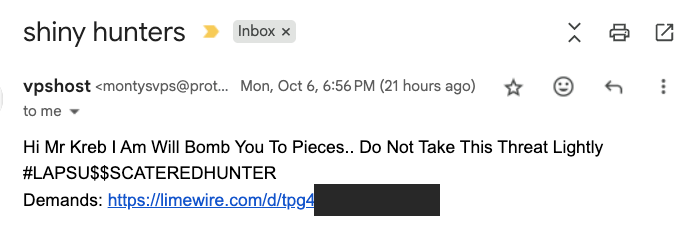
A screenshot of the phishing message linking to a malicious trojan disguised as a Windows screenshot file.
KrebsOnSecurity did not visit this link, but instead forwarded it to Mandiant, which confirmed that similar menacing missives were sent to employees at Mandiant and other security firms around the same time.
The link in the message fetches a malicious trojan disguised as a Windows screenshot file (Virustotal’s analysis on this malware is here). Simply viewing the booby-trapped screenshot image on a Windows PC is enough to cause the bundled trojan to launch in the background.
Mandiant’s Austin Larsen said the trojan is a commercially available backdoor known as ASYNCRAT, which is a .NET-based backdoor that communicates using a custom binary protocol over TCP, and can execute shell commands and download plugins to extend its features.
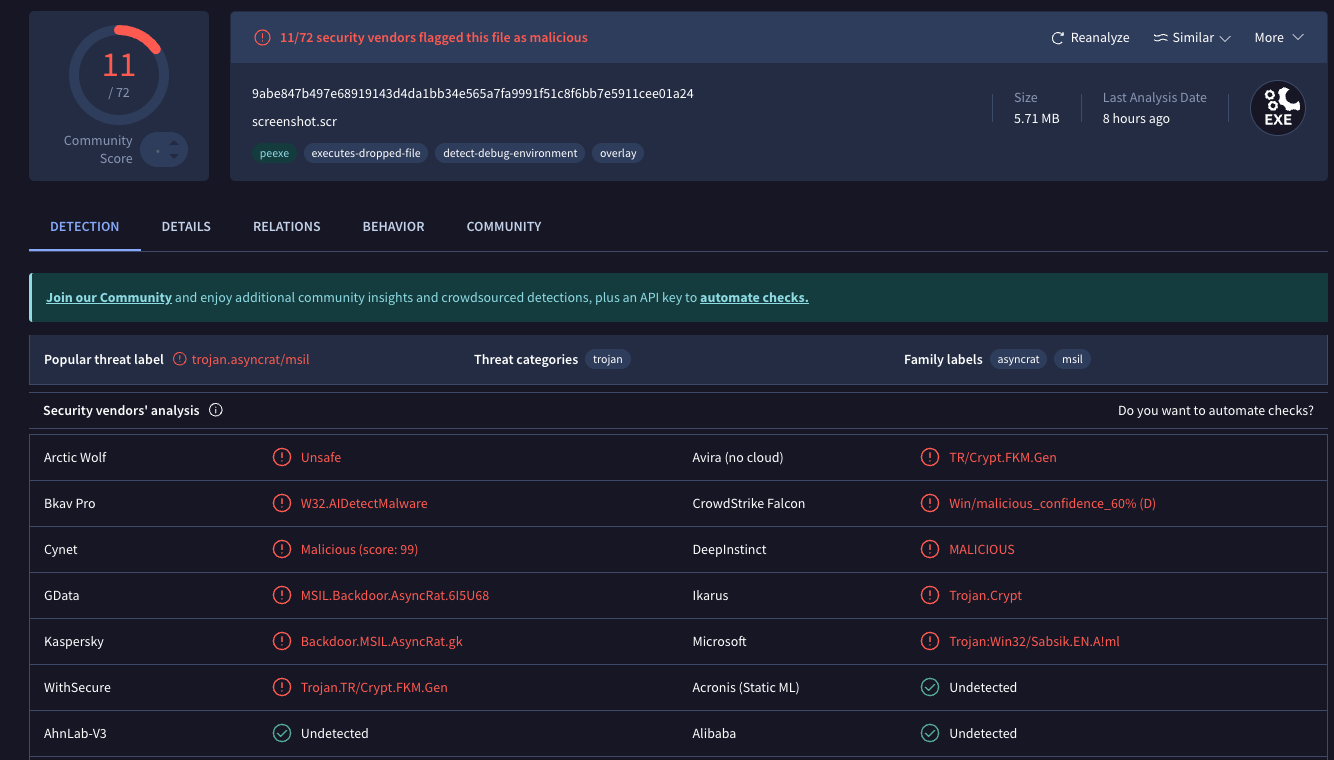
A scan of the malicious screenshot file at Virustotal.com shows it is detected as bad by nearly a dozen security and antivirus tools.
“Downloaded plugins may be executed directly in memory or stored in the registry,” Larsen wrote in an analysis shared via email. “Capabilities added via plugins include screenshot capture, file transfer, keylogging, video capture, and cryptocurrency mining. ASYNCRAT also supports a plugin that targets credentials stored by Firefox and Chromium-based web browsers.”
Malware-laced targeted emails are not out of character for certain members of the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters, who have previously harassed and threatened security researchers and even law enforcement officials who are investigating and warning about the extent of their attacks.
With so many big data breaches and ransom attacks now coming from cybercrime groups operating on the Com, law enforcement agencies on both sides of the pond are under increasing pressure to apprehend the criminal hackers involved. In late September, prosecutors in the U.K. charged two alleged Scattered Spider members aged 18 and 19 with extorting at least $115 million in ransom payments from companies victimized by data theft.
U.S. prosecutors heaped their own charges on the 19 year-old in that duo — U.K. resident Thalha Jubair — who is alleged to have been involved in data ransom attacks against Marks & Spencer and Harrods, the British foot retailer Co-op Group, and the 2023 intrusions at MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment. Jubair also was allegedly a key member of LAPSUS$, a cybercrime group that broke into dozens of technology companies beginning in late 2021.
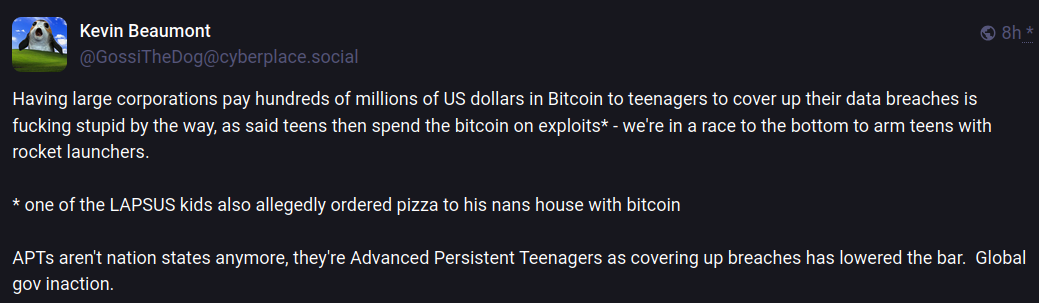
A Mastodon post by Kevin Beaumont, lamenting the prevalence of major companies paying millions to extortionist teen hackers, refers derisively to Thalha Jubair as a part of an APT threat known as “Advanced Persistent Teenagers.”
In August, convicted Scattered Spider member and 20-year-old Florida man Noah Michael Urban was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison and ordered to pay roughly $13 million in restitution to victims.
In April 2025, a 23-year-old Scottish man thought to be an early Scattered Spider member was extradited from Spain to the U.S., where he is facing charges of wire fraud, conspiracy and identity theft. U.S. prosecutors allege Tyler Robert Buchanan and co-conspirators hacked into dozens of companies in the United States and abroad, and that he personally controlled more than $26 million stolen from victims.
AI-Enabled Influence Operation Against Iran
Citizen Lab has uncovered a coordinated AI-enabled influence operation against the Iranian government, probably conducted by Israel.
Key Findings
- A coordinated network of more than 50 inauthentic X profiles is conducting an AI-enabled influence operation. The network, which we refer to as “PRISONBREAK,” is spreading narratives inciting Iranian audiences to revolt against the Islamic Republic of Iran.
- While the network was created in 2023, almost all of its activity was conducted starting in January 2025, and continues to the present day.
- The profiles’ activity appears to have been synchronized, at least in part, with the military campaign that the Israel Defense Forces conducted against Iranian targets in June 2025. ...
Mitigating AI's new risk frontier: Unifying enterprise cybersecurity with AI safety
Design for Chaos: Fastly’s Principles of Fault Isolation and Graceful Degradation
AI in the 2026 Midterm Elections
We are nearly one year out from the 2026 midterm elections, and it’s far too early to predict the outcomes. But it’s a safe bet that artificial intelligence technologies will once again be a major storyline.
The widespread fear that AI would be used to manipulate the 2024 U.S. election seems rather quaint in a year where the president posts AI-generated images of himself as the pope on official White House accounts. But AI is a lot more than an information manipulator. It’s also emerging as a politicized issue. Political first-movers are adopting the technology, and that’s opening a ...
Introducing Headlamp Plugin for Karpenter - Scaling and Visibility
Headlamp is an open‑source, extensible Kubernetes SIG UI project designed to let you explore, manage, and debug cluster resources.
Karpenter is a Kubernetes Autoscaling SIG node provisioning project that helps clusters scale quickly and efficiently. It launches new nodes in seconds, selects appropriate instance types for workloads, and manages the full node lifecycle, including scale-down.
The new Headlamp Karpenter Plugin adds real-time visibility into Karpenter’s activity directly from the Headlamp UI. It shows how Karpenter resources relate to Kubernetes objects, displays live metrics, and surfaces scaling events as they happen. You can inspect pending pods during provisioning, review scaling decisions, and edit Karpenter-managed resources with built-in validation. The Karpenter plugin was made as part of a LFX mentor project.
The Karpenter plugin for Headlamp aims to make it easier for Kubernetes users and operators to understand, debug, and fine-tune autoscaling behavior in their clusters. Now we will give a brief tour of the Headlamp plugin.
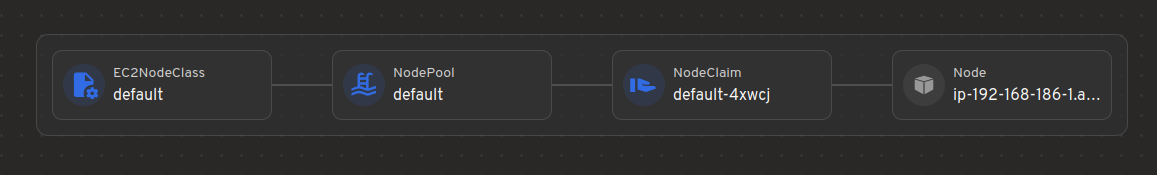
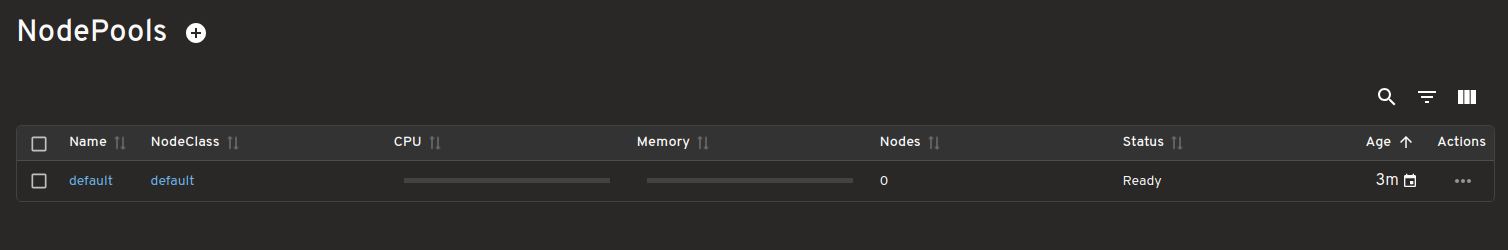
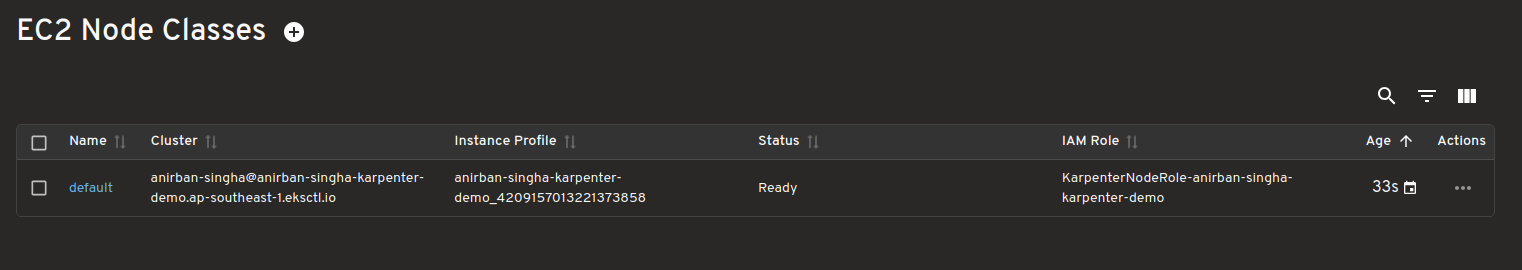
Map view of Karpenter Resources and how they relate to Kubernetes resources
Easily see how Karpenter Resources like NodeClasses, NodePool and NodeClaims connect with core Kubernetes resources like Pods, Nodes etc.
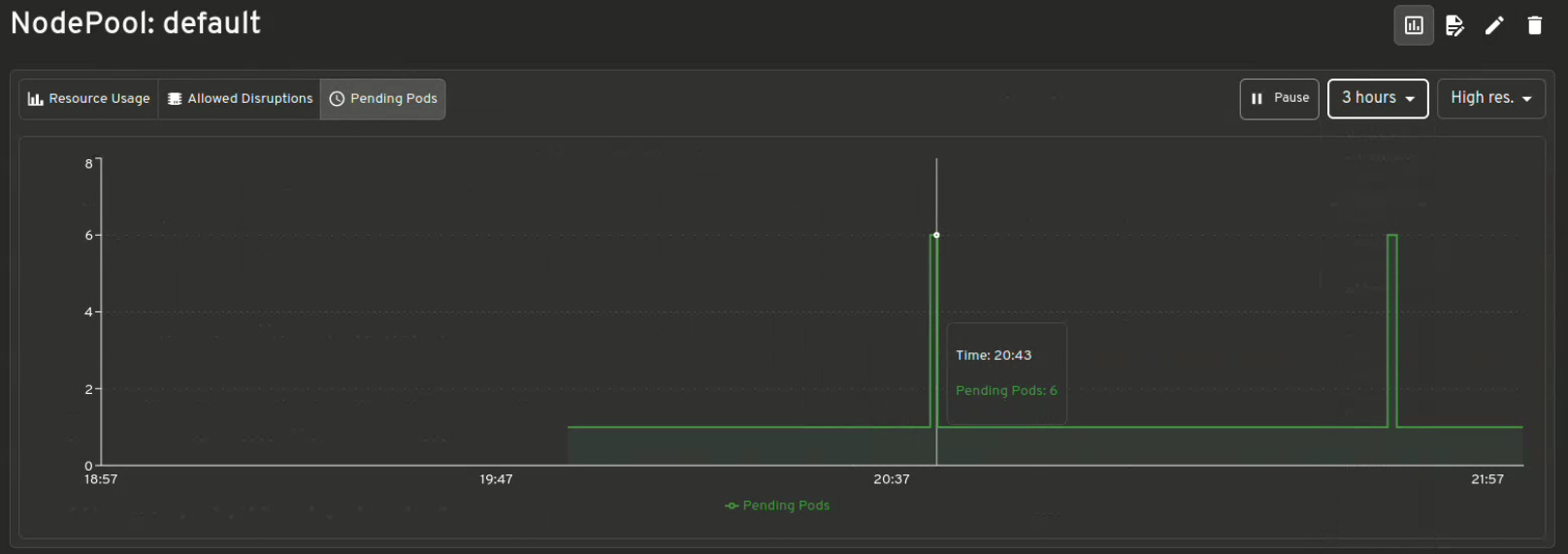
Visualization of Karpenter Metrics
Get instant insights of Resource Usage v/s Limits, Allowed disruptions, Pending Pods, Provisioning Latency and many more .
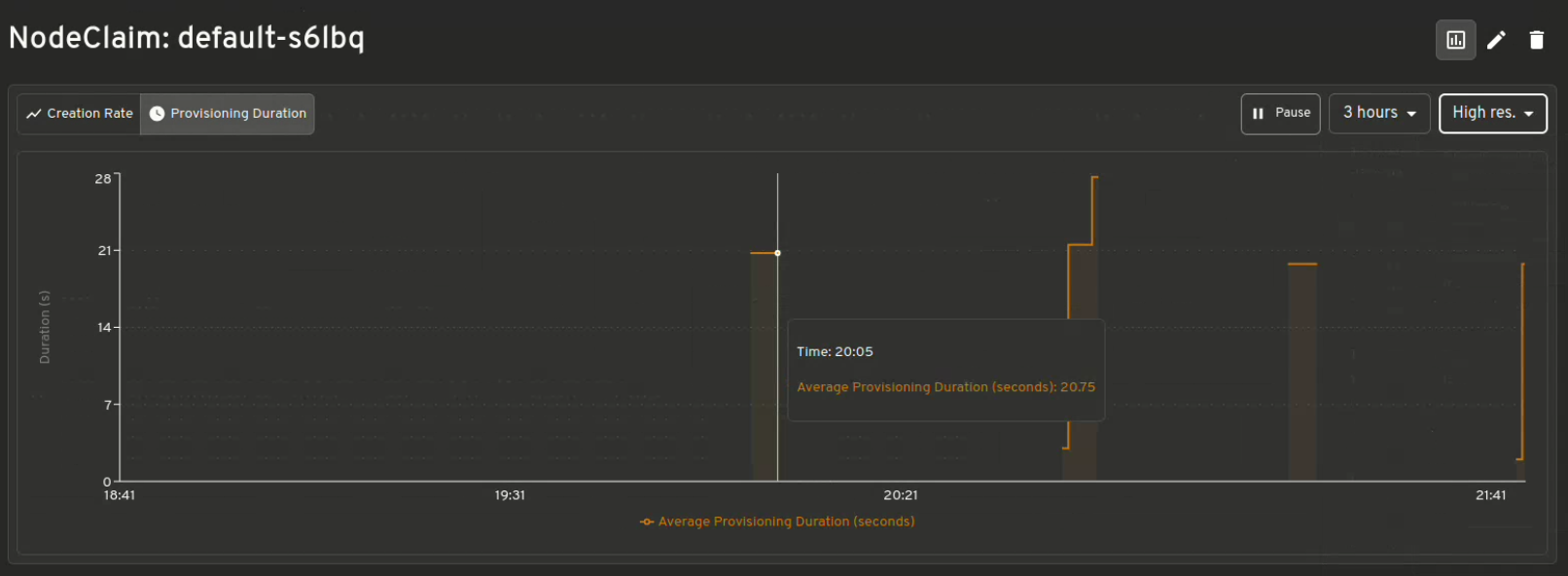
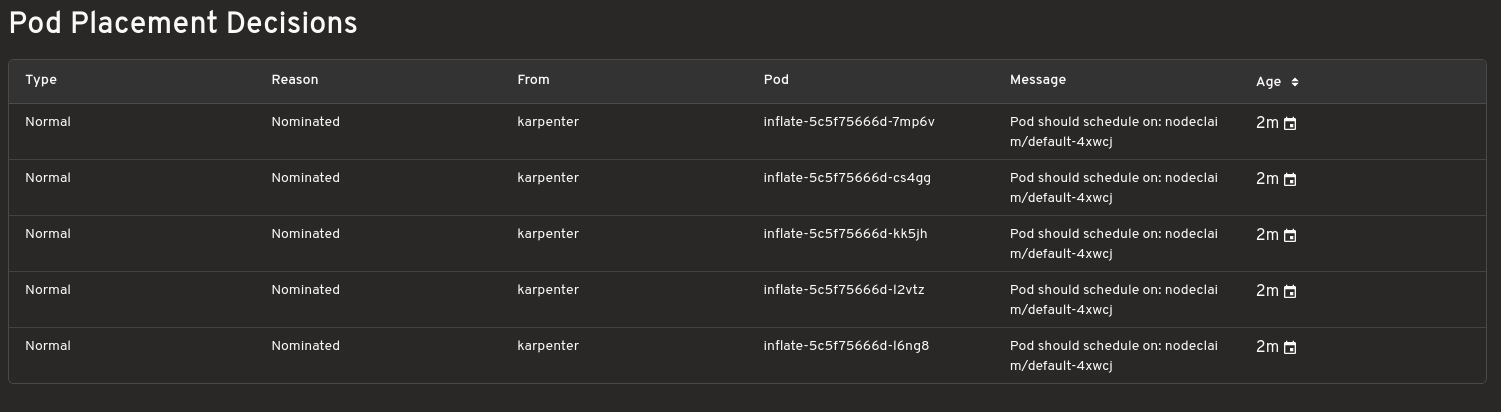
Scaling decisions
Shows which instances are being provisioned for your workloads and understand the reason behind why Karpenter made those choices. Helpful while debugging.
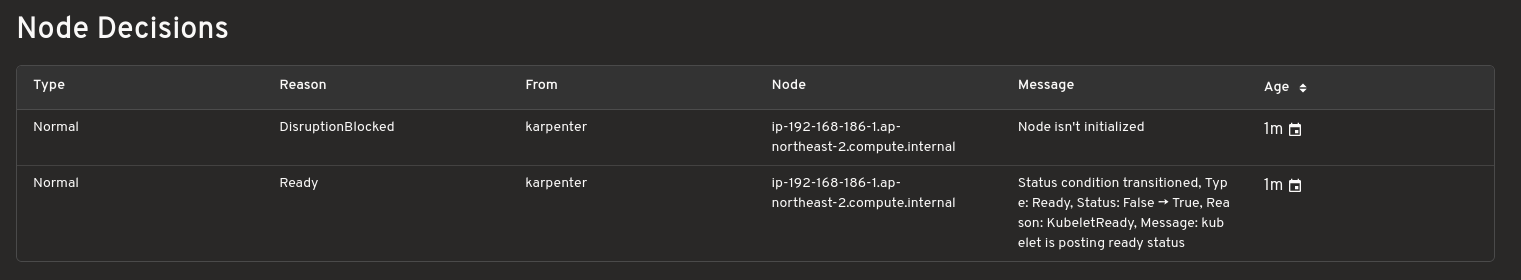
Config editor with validation support
Make live edits to Karpenter configurations. The editor includes diff previews and resource validation for safer adjustments.
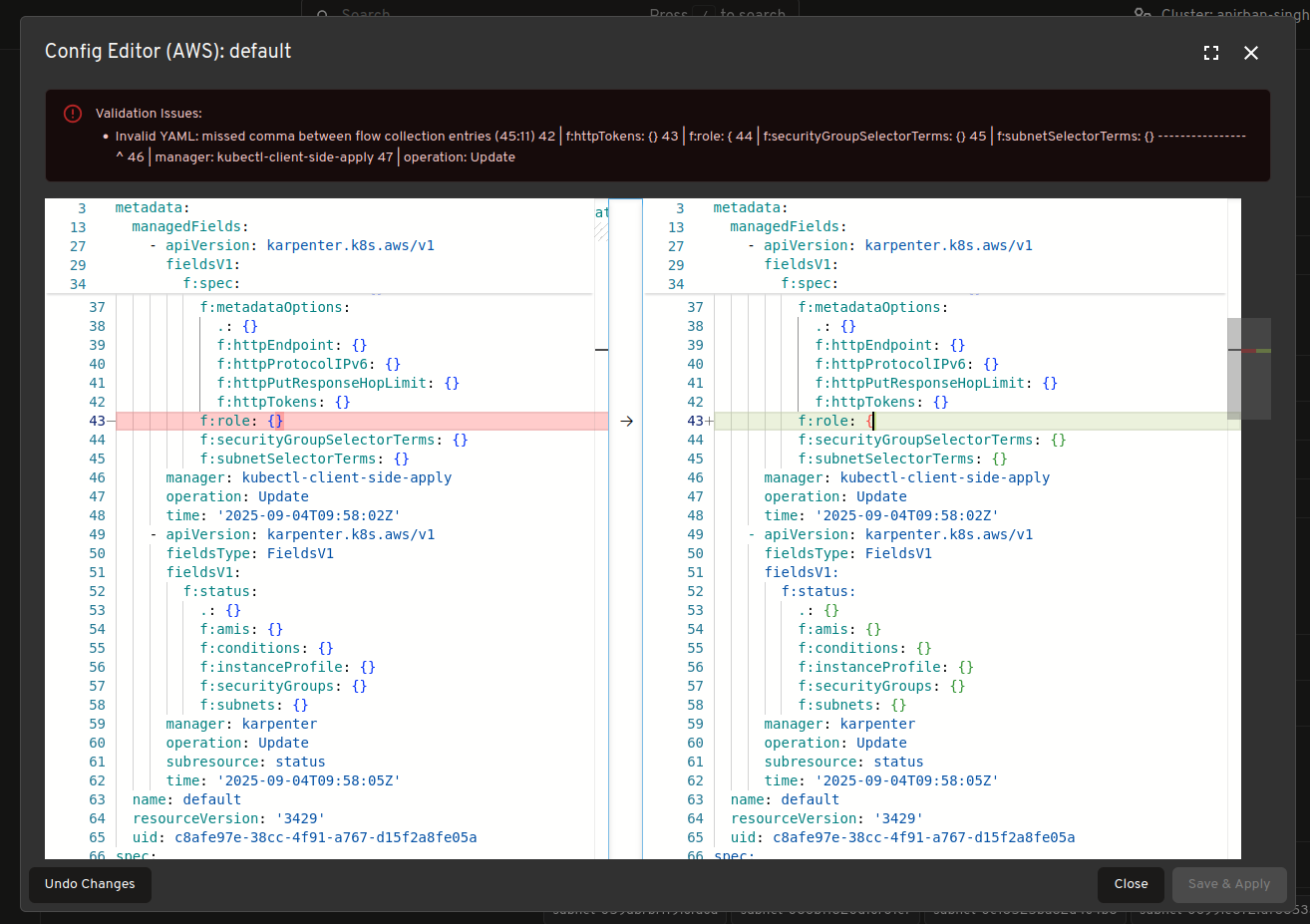
Real time view of Karpenter resources
View and track Karpenter specific resources in real time such as “NodeClaims” as your cluster scales up and down.
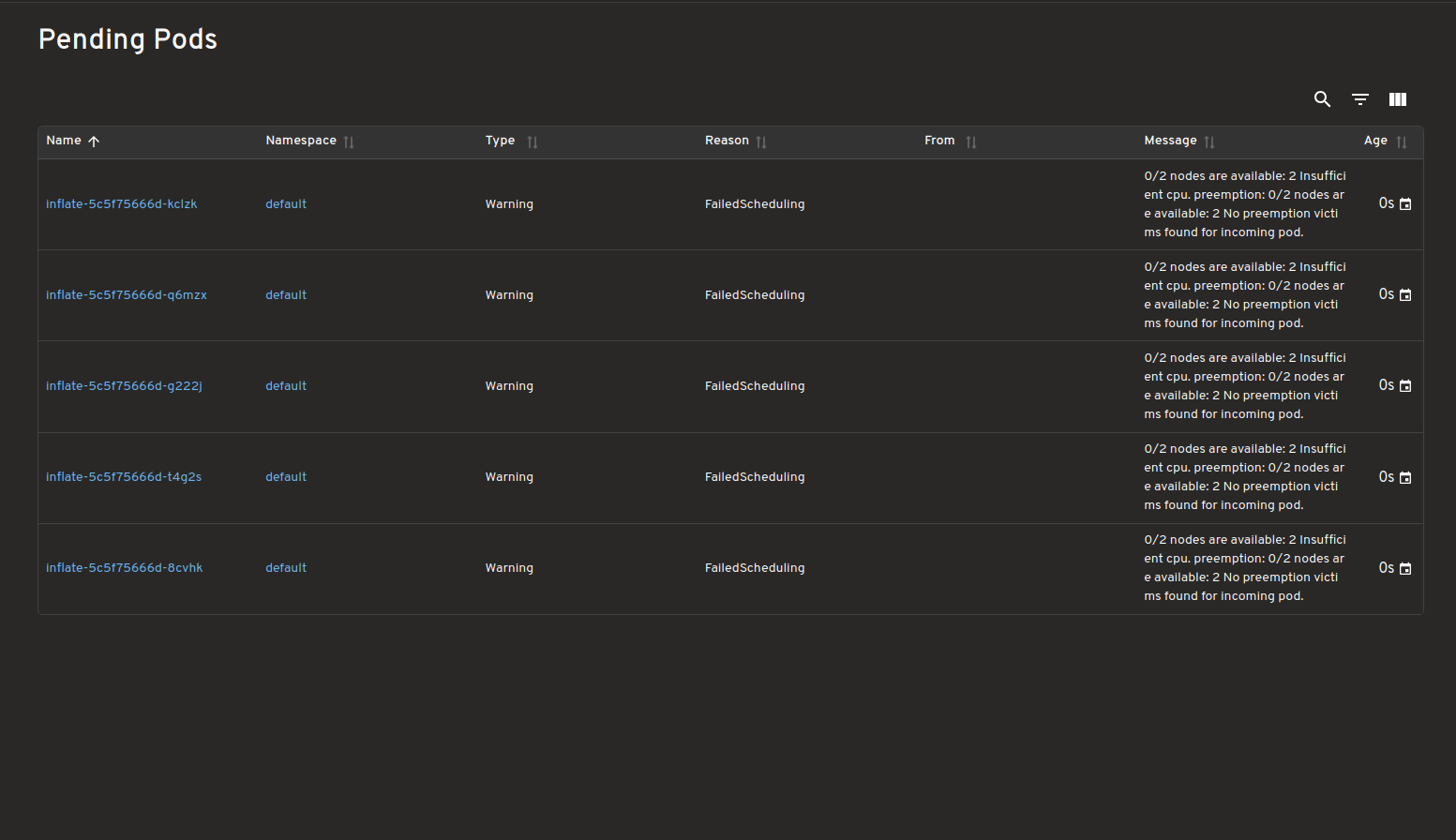
Dashboard for Pending Pods
View all pending pods with unmet scheduling requirements/Failed Scheduling highlighting why they couldn't be scheduled.
Karpenter Providers
This plugin should work with most Karpenter providers, but has only so far been tested on the ones listed in the table. Additionally, each provider gives some extra information, and the ones in the table below are displayed by the plugin.
Provider Name Tested Extra provider specific info supported AWS ✅ ✅ Azure ✅ ✅ AlibabaCloud ❌ ❌ Bizfly Cloud ❌ ❌ Cluster API ❌ ❌ GCP ❌ ❌ Proxmox ❌ ❌ Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) ❌ ❌Please submit an issue if you test one of the untested providers or if you want support for this provider (PRs also gladly accepted).
How to use
Please see the plugins/karpenter/README.md for instructions on how to use.
Feedback and Questions
Please submit an issue if you use Karpenter and have any other ideas or feedback. Or come to the Kubernetes slack headlamp channel for a chat.
CoreDNS-1.13.0 Release
Autonomous Testing of etcd's Robustness
This is a post from the CNCF blog which we are sharing with our community as well.
As a critical component of many production systems, including Kubernetes, the etcd project’s first priority is reliability. Ensuring consistency and data safety requires our project contributors to continuously improve testing methodologies. In this article, we will describe how we used advanced simulation testing to uncover subtle bugs, validate the robustness of our releases, and increase our confidence in etcd’s stability. We’ll share our key findings and how they have improved etcd.
Daniel Miessler on the AI Attack/Defense Balance
His conclusion:
Context wins
Basically whoever can see the most about the target, and can hold that picture in their mind the best, will be best at finding the vulnerabilities the fastest and taking advantage of them. Or, as the defender, applying patches or mitigations the fastest.
And if you’re on the inside you know what the applications do. You know what’s important and what isn’t. And you can use all that internal knowledge to fix things—hopefully before the baddies take advantage.
Summary and prediction
- Attackers will have the advantage for 3-5 years. For less-advanced defender teams, this will take much longer. ...
How Red Hat can support your journey to a standard operating environment
Security update: Incident related to Red Hat Consulting GitLab instance
Fluentd to Fluent Bit: A Migration Guide
Fluentd was created over 14 years ago and still continues to be one of the most widely deployed technologies for log collection in the enterprise. Fluentd’s distributed plugin architecture and highly permissive licensing made it ideal as part of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) as a now graduated project.
However, enterprises drowning in telemetry data are now requiring solutions that have higher performance, more native support for evolving schemas and formats, and increased flexibility in processing. Enter Fluent Bit.
When and why to migrate?
Fluent Bit, while initially growing as a sub-project within the Fluent ecosystem, expanded from Fluentd to support all telemetry types – logs, metrics, and traces. Fluent Bit now is the more popular of the two with over 15 billion deployments and used by Amazon, Google, Oracle and Microsoft to name a few.
Fluent Bit also is fully aligned with OpenTelemetry signals, format and protocol, which ensures that users will be able to continue handling telemetry data as it grows and evolves.
Among the most frequent questions we get as the maintainers of the projects are:
- How do we migrate?
- What should we watch out for?
- And what business value do we get for migrating?
This article aims to answer these questions with examples. We want to help make it an easy decision to migrate from Fluentd to Fluent Bit.
Why Migrate?
Here is a quick list of the reasons users switch from Fluentd to Fluent Bit:
- Higher performance for the same resources you are already using
- Full OpenTelemetry support for logs, metrics, and traces as well as Prometheus support for metrics
- Simpler configuration and routing ability to multiple locations
- Higher velocity for adding custom processing rules
- Integrated monitoring to better understand performance and dataflows
Fluentd vs. Fluent Bit: What are the Differences
Background
To understand all the differences between the projects, it is important to understand the background of each project and the era it was built for. With Fluentd, the main language is Ruby and initially designed to help users push data to big data platforms such as Hadoop.The project follows a distributed architecture, where plugins are installed after the main binary is installed and deployed.
Fluent Bit on the other hand, is written in C, with a focus on hyper performance in smaller systems (containers, embedded Linux). The project learned from Fluentd’s plugins and instead opts for fully embedded plugins that are part of the core binary.
Performance
The obvious difference and main value of switching from Fluentd to Fluent Bit is the performance. With Fluent Bit, the amount of logs you can process with the same resources could be anywhere from 10 to 40 times greater depending on the plugin you are using.
Fluent Bit was written from the ground up to be hyper performant, with a focus of shipping data as fast as possible for data analysis. Later on, performance was found to be efficient enough that more edge processing could be added without compromising on the mission to make the agent as fast as possible.
Routing
Other parts of Fluent Bit evolved from challenges encountered with Fluentd, such as buffering and routing. With Fluentd multirouting was an afterthought and users needed to “copy” the data streams to route data to multiple points.
This made configuration management a nightmare, in addition to essentially duplicating the resource requirements for routing that data.
In Fluent Bit the buffers are stored once, which allows multiple plugins to “subscribe” to a stream of data. This ensures that data is stored once and subscribed many times allowing for multirouting without the trade-offs of performance and configuration fatigue.
Telemetry signal focus
While Fluentd was initially a data shipper, it grew into a logging agent used within projects such as Kubernetes and companies like Splunk. Fluent Bit on the other hand started as an embedded metrics collector with log files coming in after. As Fluent Bit adoption started to outweigh Fluentd’s functionality, capabilities such as OpenTelemetry logs/metrics/traces, Prometheus Scrape and Remote Write Support, eBPF and profiling support were all added.
Today Fluent Bit is aligned with OpenTelemetry schema, formats and protocols and meant to be a lightweight implementation that is highly performant.
Custom processing
Fluentd and Fluent Bit have many of the same processor names, but when it comes to custom processing the options are quite different.
With Fluentd the option is `enable_ruby`, which allows custom Ruby scripts within a configuration to perform actions. This can work effectively for small tasks; however it has a large penalty as logic gets more complicated, adding more performance bottlenecks.
With Fluent Bit, custom processing is done in the language Lua, which gives tremendous flexibility. However, unlike Fluentd, Fluent Bit’s Lua processor is quite performant and can be used at scale (100+ TB/day).
Custom plugins
Both projects allow custom plugins to help you connect with your source or destination. With Fluentd, these custom plugins are “Ruby Gems” that you can download and install into existing or new installations or deployments. With Fluent Bit, custom plugins are written and compiled in Go. There are also new initiatives for writing custom plugins in any language you want and compiling them into WebAssembly.
One lesson we learned from Fluentd’s distributed plugin architecture was the number of plugins can increase exponentially. However, the quality and maintenance required generally left many of the plugins abandoned and unsupported. With Fluent Bit, plugins are all incorporated into the source code itself, which ensures compatibility with every release.
Custom plugins still remain independent of the main repository. However, we are looking at ways to allow these to also share the same benefit of native C plugins within the main GitHub repository.
Monitoring
Understanding how data is traversing your environment is generally a top request from users who deploy Fluentd or Fluent Bit. With Fluentd, enabling these settings could require complicated configuration via “monitor_agent” or using a third party prometheus exporter plugin. These monitoring plugins also add maintenance overhead for Fluentd, which can affect performance.
Fluent Bit has monitoring as part of its core functionality and is retrievable via a native plugin (`fluentbit_metrics`) or scrapeable on an HTTP port. Fluent Bit’s metrics also incorporate more information than Fluentd’s, which allows you to understand bytes, records, storage and connection information.
How to get started with a Fluentd to Fluent Bit migration
The next question we’re answering is: How do you get started?
The first important step is to understand how Fluentd is deployed, what processing happens in the environment and where data is flowing.
What you don’t need to worry about:
- Architecture support: Both applications support x86 and ARM.
- Platform support: Fluent Bit supports the same and more as Fluentd does today. Legacy systems may differ, however it is important to note those are not maintained in either OSS project.
- Regular expressions: If you built a large library of regular expressions using the Onigmo parser library, you can rest comfortably knowing that Fluent Bit supports it.
Deployment
Deployed as an Agent (Linux or Windows Package)
When Fluentd is deployed as an agent on Linux or Windows, its primary function is to collect local log files or Windows event logs and route them to a particular destination.Thankfully, Fluent Bit’s local collection capabilities are equal to Fluentd’s, including the ability to resume on failure, store last log lines collected and local buffering.
Deployed in Kubernetes as a DaemonSet
If Fluentd is running as a DaemonSet in your Kubernetes cluster, you should first check the image that is running. As Fluentd has distributed plugins, the DaemonSet image may have specific plugins included, which ensures you can go directly from reading Kubernetes logs to the end destination.
This example has OpenSearch and Kafka included as plugins, so you should validate that the image you are using has the same plugins as Fluent Bit. Fluent Bit also supports Kubernetes enrichment on all logs, giving data around namespace, pod, labels and more.
Deployed as an Aggregator / Collector
If your Fluentd is deployed collecting logs from syslog, network devices or HTTP requests, you can first verify that Fluent Bit has the same capability. For example, Fluent Bit has syslog, TCP, HTTP and UDP plugins that can cover a majority of these use cases.
In addition, Fluent Bit also can receive OpenTelemetry HTTP1/gRPC, Prometheus Remote Write, HTTP gzip and Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC) as additional inbound signals.
Adding a Telemetry Pipeline
When migrating from Fluentd to Fluent Bit, we would also recommend looking at adding a Telemetry Pipeline in the middle of the agents and the destinations. This allows you to move larger pieces of processing logic within Fluentd agents downstream.
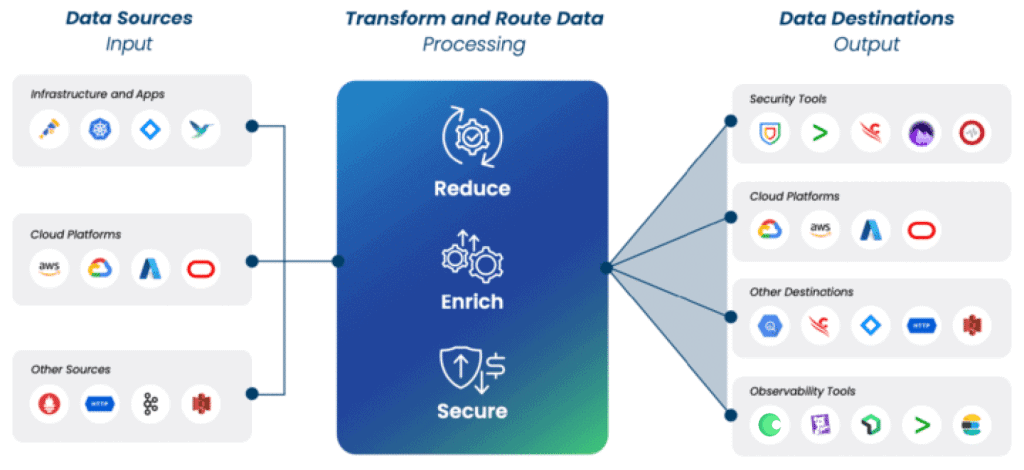
Configuration
The configuration syntax between Fluentd and Fluent Bit is vastly different. While both have started to support YAML more recently, most legacy Fluentd configurations will still be written in the domain-specific configuration language that is XML-esque.
Some general notes:
- Look at validating a single plugin at a time, and then at expanding to a single route (such as system logs to OpenSearch).
- Buffering and thread settings are not as important within Fluent Bit.
- Security settings should be similar.
When in doubt, reaching out to the Fluent community is useful in helping with some of the more granular settings.
Custom Plugins
When migrating, it’s important to ensure that Fluent Bit supports all plugins (sources and destinations). You should also check that it supports particular settings around authentication, authorization or access. This will be a manual process that can take some time. However, this will also allow you a chance to revisit decisions on specific data formats or plugin settings that you made in the past.
Custom Processing Logic
If you have labels, filters or other processing logic within Fluentd, it is important to note the functionality you are trying to achieve. While it may seem like just swapping those filters over might be easiest, you should also look at ways to migrate those directly into Fluent Bit processors. If you have a significant amount of custom Ruby, you can use large language models (LLMs) to help convert it into suitable Lua.
Migrating Portions at a Time
You don’t need to migrate all your functionality at once. Because Fluent Bit is lightweight and performant, you can look at ways to have each agent handle different portions of the workload. Over time you can follow the logic above to continue migrating without having to worry about log collection disruptions.
Conclusion
While migrating from Fluentd to Fluent Bit might seem like an enormous task, you have many options about how to attack and where to focus to achieve the highest impact. Of course migrations are also a great time to re-evaluate certain logic for improvement and even introduce new architecture patterns such as a telemetry pipeline.
If you are looking for guided or assisted help, let me know. I have helped many folks migrate from Fluentd to Fluent Bit and even assisted with modernizing certain portions to a telemetry pipeline.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why migrate from Fluentd to Fluent Bit
With Fluent Bit you will get higher performance for the same resources you are already using; full OpenTelemetry support for logs, metrics, and traces as well as Prometheus support for metrics; simpler configuration and routing ability to multiple locations; higher velocity for adding custom processing rules; and integrated monitoring to better understand performance and dataflows.
What are some differences between Fluentd and Fluent Bit?
With Fluentd, the main language is Ruby and initially designed to help users push data to big data platforms such as Hadoop. Meanwhile, Fluent Bit is written in C, with a focus on hyper performance in smaller systems (containers, embedded Linux).
Can Fluentd and Fluent Bit work together?
Yes Fluent Bit and Fluentd can work together, which means it’s possible to capture from more sources by using Fluentd and introduce the data into a Fluent Bit deployment. The Forward plugin has a defined standard that Fluent Bit and Fluentd both use. Some external products have also adopted this protocol so they can be connected directly to Fluent Bit.
Use of Generative AI in Scams
New report: “Scam GPT: GenAI and the Automation of Fraud.”
This primer maps what we currently know about generative AI’s role in scams, the communities most at risk, and the broader economic and cultural shifts that are making people more willing to take risks, more vulnerable to deception, and more likely to either perpetuate scams or fall victim to them.
AI-enhanced scams are not merely financial or technological crimes; they also exploit social vulnerabilities whether short-term, like travel, or structural, like precarious employment. This means they require social solutions in addition to technical ones. By examining how scammers are changing and accelerating their methods, we hope to show that defending against them will require a constellation of cultural shifts, corporate interventions, and effective legislation...
GKE 10 years and SIG Networking, With Antonio Ojea
Today we talk to Antonio Ojea. Antonio is a software engineer at Google and one of the core maintainers of Kubernetes. He is one of the Tech Lead of SIG Networking and Testing and a member of the Steering Committee.
Do you have something cool to share? Some questions? Let us know:
- web: kubernetespodcast.com
- mail: [email protected]
- twitter: @kubernetespod
- bluesky: @kubernetespodcast.com
News of the week
Fastly's Seven Years of Recognition as a Gartner® Peer Insights™ Customers’ Choice
Kubewarden 1.29 Release
Details of a Scam
Longtime Crypto-Gram readers know that I collect personal experiences of people being scammed. Here’s an almost:
Then he added, “Here at Chase, we’ll never ask for your personal information or passwords.” On the contrary, he gave me more information—two “cancellation codes” and a long case number with four letters and 10 digits.
That’s when he offered to transfer me to his supervisor. That simple phrase, familiar from countless customer-service calls, draped a cloak of corporate competence over this unfolding drama. His supervisor. I mean, would a scammer have a supervisor?...