Feed aggregator
The Cloudflare Outage May Be a Security Roadmap
An intermittent outage at Cloudflare on Tuesday briefly knocked many of the Internet’s top destinations offline. Some affected Cloudflare customers were able to pivot away from the platform temporarily so that visitors could still access their websites. But security experts say doing so may have also triggered an impromptu network penetration test for organizations that have come to rely on Cloudflare to block many types of abusive and malicious traffic.
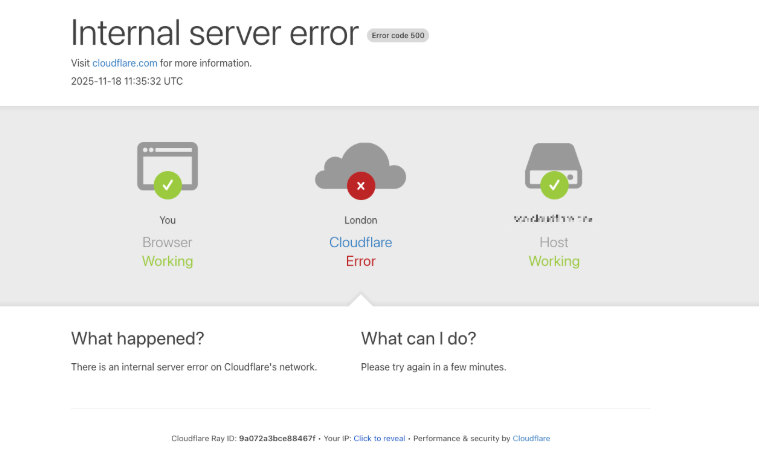
At around 6:30 EST/11:30 UTC on Nov. 18, Cloudflare’s status page acknowledged the company was experiencing “an internal service degradation.” After several hours of Cloudflare services coming back up and failing again, many websites behind Cloudflare found they could not migrate away from using the company’s services because the Cloudflare portal was unreachable and/or because they also were getting their domain name system (DNS) services from Cloudflare.
However, some customers did manage to pivot their domains away from Cloudflare during the outage. And many of those organizations probably need to take a closer look at their web application firewall (WAF) logs during that time, said Aaron Turner, a faculty member at IANS Research.
Turner said Cloudflare’s WAF does a good job filtering out malicious traffic that matches any one of the top ten types of application-layer attacks, including credential stuffing, cross-site scripting, SQL injection, bot attacks and API abuse. But he said this outage might be a good opportunity for Cloudflare customers to better understand how their own app and website defenses may be failing without Cloudflare’s help.
“Your developers could have been lazy in the past for SQL injection because Cloudflare stopped that stuff at the edge,” Turner said. “Maybe you didn’t have the best security QA [quality assurance] for certain things because Cloudflare was the control layer to compensate for that.”
Turner said one company he’s working with saw a huge increase in log volume and they are still trying to figure out what was “legit malicious” versus just noise.
“It looks like there was about an eight hour window when several high-profile sites decided to bypass Cloudflare for the sake of availability,” Turner said. “Many companies have essentially relied on Cloudflare for the OWASP Top Ten [web application vulnerabilities] and a whole range of bot blocking. How much badness could have happened in that window? Any organization that made that decision needs to look closely at any exposed infrastructure to see if they have someone persisting after they’ve switched back to Cloudflare protections.”
Turner said some cybercrime groups likely noticed when an online merchant they normally stalk stopped using Cloudflare’s services during the outage.
“Let’s say you were an attacker, trying to grind your way into a target, but you felt that Cloudflare was in the way in the past,” he said. “Then you see through DNS changes that the target has eliminated Cloudflare from their web stack due to the outage. You’re now going to launch a whole bunch of new attacks because the protective layer is no longer in place.”
Nicole Scott, senior product marketing manager at the McLean, Va. based Replica Cyber, called yesterday’s outage “a free tabletop exercise, whether you meant to run one or not.”
“That few-hour window was a live stress test of how your organization routes around its own control plane and shadow IT blossoms under the sunlamp of time pressure,” Scott said in a post on LinkedIn. “Yes, look at the traffic that hit you while protections were weakened. But also look hard at the behavior inside your org.”
Scott said organizations seeking security insights from the Cloudflare outage should ask themselves:
1. What was turned off or bypassed (WAF, bot protections, geo blocks), and for how long?
2. What emergency DNS or routing changes were made, and who approved them?
3. Did people shift work to personal devices, home Wi-Fi, or unsanctioned Software-as-a-Service providers to get around the outage?
4. Did anyone stand up new services, tunnels, or vendor accounts “just for now”?
5. Is there a plan to unwind those changes, or are they now permanent workarounds?
6. For the next incident, what’s the intentional fallback plan, instead of decentralized improvisation?
In a postmortem published Tuesday evening, Cloudflare said the disruption was not caused, directly or indirectly, by a cyberattack or malicious activity of any kind.
“Instead, it was triggered by a change to one of our database systems’ permissions which caused the database to output multiple entries into a ‘feature file’ used by our Bot Management system,” Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince wrote. “That feature file, in turn, doubled in size. The larger-than-expected feature file was then propagated to all the machines that make up our network.”
Cloudflare estimates that roughly 20 percent of websites use its services, and with much of the modern web relying heavily on a handful of other cloud providers including AWS and Azure, even a brief outage at one of these platforms can create a single point of failure for many organizations.
Martin Greenfield, CEO at the IT consultancy Quod Orbis, said Tuesday’s outage was another reminder that many organizations may be putting too many of their eggs in one basket.
“There are several practical and overdue fixes,” Greenfield advised. “Split your estate. Spread WAF and DDoS protection across multiple zones. Use multi-vendor DNS. Segment applications so a single provider outage doesn’t cascade. And continuously monitor controls to detect single-vendor dependency.”
Legal Restrictions on Vulnerability Disclosure
Kendra Albert gave an excellent talk at USENIX Security this year, pointing out that the legal agreements surrounding vulnerability disclosure muzzle researchers while allowing companies to not fix the vulnerabilities—exactly the opposite of what the responsible disclosure movement of the early 2000s was supposed to prevent. This is the talk.
Thirty years ago, a debate raged over whether vulnerability disclosure was good for computer security. On one side, full disclosure advocates argued that software bugs weren’t getting fixed and wouldn’t get fixed if companies that made insecure software wasn’t called out publicly. On the other side, companies argued that full disclosure led to exploitation of unpatched vulnerabilities, especially if they were hard to fix. After blog posts, public debates, and countless mailing list flame wars, there emerged a compromise solution: coordinated vulnerability disclosure, where vulnerabilities were disclosed after a period of confidentiality where vendors can attempt to fix things. Although full disclosure fell out of fashion, disclosure won and security through obscurity lost. We’ve lived happily ever after since...
Outages, Attacks, and a Need for Resilience
A Function Inliner for Wasmtime and Cranelift
AI and Voter Engagement
Social media has been a familiar, even mundane, part of life for nearly two decades. It can be easy to forget it was not always that way.
In 2008, social media was just emerging into the mainstream. Facebook reached 100 million users that summer. And a singular candidate was integrating social media into his political campaign: Barack Obama. His campaign’s use of social media was so bracingly innovative, so impactful, that it was viewed by journalist David Talbot and others as the strategy that enabled the first term Senator to win the White House...
Automation unleashed: Introducing the new Red Hat Certified Ansible Collection amazon.ai for generative AI
Enhance workload security with confidential containers on Azure Red Hat OpenShift
Introducing the Kubewarden JavaScript/TypeScript SDK
More Prompt||GTFO
The next three in this series on online events highlighting interesting uses of AI in cybersecurity are online: #4, #5, and #6. Well worth watching.
Helm 4 Released
On Wednesday November 12th, during the Helm 4 presentation at KubeCon + CloudNativeCon, Helm v4.0.0 was released. This is the first new major version of Helm in 6 years.
What's New
Helm v3 has served the Kubernetes community well for many years. During that time we saw new ways to use Helm, new applications installed via charts, the rise of Artifact Hub, and numerous tools that build on top of Helm. We also saw where we wanted to add features but the internal architecture of Helm didn't provide a path forward without breaking public APIs in the SDK. Helm 4 makes those changes to enable new features now and into the future.
Some of the new features include:
- Redesigned plugin system that supports Web Assembly based plugins
- Post-renderers are now plugins
- Server side apply is now supported
- Improved resource watching, to support waiting, based on kstatus
- Local Content-based caching (e.g. for charts)
- Logging via slog enabling SDK logging to integrate with modern loggers
- Reproducible/Idempotent builds of chart archives
- Updated SDK API including support for multiple chart API versions (new experimental v3 chart API version coming soon)
You can learn about more of the changes in the Helm 4 Overview.
Helm v3 Support
When a major version of software comes out, it takes awhile to make the transition. Helm v3 will continue to be supported to enable a clean transition period. The dates of continued support are:
- Bug fixes until July 8th 2026.
- Security fixes until November 11th 2026.
Helm releases updates on Wednesdays (typically the 2nd Wednesday in a month) and these dates correspond with release schedule dates. During this time there will be NO features backported other than updates to the Kubernetes client libraries that enable support of new Kubernetes versions.
Learn More
You can learn about the Helm changes in the overview or find all the changes in the full changelog. The documentation shares many more details as you can find all the ways Helm has stayed the same and the new features you can take advantage of.
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, November 2025 Edition
Microsoft this week pushed security updates to fix more than 60 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and supported software, including at least one zero-day bug that is already being exploited. Microsoft also fixed a glitch that prevented some Windows 10 users from taking advantage of an extra year of security updates, which is nice because the zero-day flaw and other critical weaknesses affect all versions of Windows, including Windows 10.

Affected products this month include the Windows OS, Office, SharePoint, SQL Server, Visual Studio, GitHub Copilot, and Azure Monitor Agent. The zero-day threat concerns a memory corruption bug deep in the Windows innards called CVE-2025-62215. Despite the flaw’s zero-day status, Microsoft has assigned it an “important” rating rather than critical, because exploiting it requires an attacker to already have access to the target’s device.
“These types of vulnerabilities are often exploited as part of a more complex attack chain,” said Johannes Ullrich, dean of research for the SANS Technology Institute. “However, exploiting this specific vulnerability is likely to be relatively straightforward, given the existence of prior similar vulnerabilities.”
Ben McCarthy, lead cybersecurity engineer at Immersive, called attention to CVE-2025-60274, a critical weakness in a core Windows graphic component (GDI+) that is used by a massive number of applications, including Microsoft Office, web servers processing images, and countless third-party applications.
“The patch for this should be an organization’s highest priority,” McCarthy said. “While Microsoft assesses this as ‘Exploitation Less Likely,’ a 9.8-rated flaw in a ubiquitous library like GDI+ is a critical risk.”
Microsoft patched a critical bug in Office — CVE-2025-62199 — that can lead to remote code execution on a Windows system. Alex Vovk, CEO and co-founder of Action1, said this Office flaw is a high priority because it is low complexity, needs no privileges, and can be exploited just by viewing a booby-trapped message in the Preview Pane.
Many of the more concerning bugs addressed by Microsoft this month affect Windows 10, an operating system that Microsoft officially ceased supporting with patches last month. As that deadline rolled around, however, Microsoft began offering Windows 10 users an extra year of free updates, so long as they register their PC to an active Microsoft account.
Judging from the comments on last month’s Patch Tuesday post, that registration worked for a lot of Windows 10 users, but some readers reported the option for an extra year of updates was never offered. Nick Carroll, cyber incident response manager at Nightwing, notes that Microsoft has recently released an out-of-band update to address issues when trying to enroll in the Windows 10 Consumer Extended Security Update program.
“If you plan to participate in the program, make sure you update and install KB5071959 to address the enrollment issues,” Carroll said. “After that is installed, users should be able to install other updates such as today’s KB5068781 which is the latest update to Windows 10.”
Chris Goettl at Ivanti notes that in addition to Microsoft updates today, third-party updates from Adobe and Mozilla have already been released. Also, an update for Google Chrome is expected soon, which means Edge will also be in need of its own update.
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a clickable breakdown of each individual fix from Microsoft, indexed by severity and CVSS score. Enterprise Windows admins involved in testing patches before rolling them out should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the skinny on any updates gone awry.
As always, please don’t neglect to back up your data (if not your entire system) at regular intervals, and feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these fixes.
[Author’s note: This post was intended to appear on the homepage on Tuesday, Nov. 11. I’m still not sure how it happened, but somehow this story failed to publish that day. My apologies for the oversight.]
Friday Squid Blogging: Pilot Whales Eat a Lot of Squid
Short-finned pilot wales (Globicephala macrorhynchus) eat at lot of squid:
To figure out a short-finned pilot whale’s caloric intake, Gough says, the team had to combine data from a variety of sources, including movement data from short-lasting tags, daily feeding rates from satellite tags, body measurements collected via aerial drones, and sifting through the stomachs of unfortunate whales that ended up stranded on land.
Once the team pulled all this data together, they estimated that a typical whale will eat between 82 and 202 squid a day. To meet their energy needs, a whale will have to consume an average of 140 squid a day. Annually, that’s about 74,000 squid per whale. For all the whales in the area, that amounts to about 88,000 tons of squid eaten every year...
Upcoming Speaking Engagements
This is a current list of where and when I am scheduled to speak:
- My coauthor Nathan E. Sanders and I are speaking at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington, DC at noon ET on November 17, 2025. The event is hosted by the POPVOX Foundation and the topic is “AI and Congress: Practical Steps to Govern and Prepare.”
- I’m speaking on “Integrity and Trustworthy AI” at North Hennepin Community College in Brooklyn Park, Minnesota, USA, on Friday, November 21, 2025, at 2:00 PM CT. The event is cohosted by the college and The Twin Cities IEEE Computer Society...
The Role of Humans in an AI-Powered World
As AI capabilities grow, we must delineate the roles that should remain exclusively human. The line seems to be between fact-based decisions and judgment-based decisions.
For example, in a medical context, if an AI was demonstrably better at reading a test result and diagnosing cancer than a human, you would take the AI in a second. You want the more accurate tool. But justice is harder because justice is inherently a human quality in a way that “Is this tumor cancerous?” is not. That’s a fact-based question. “What’s the right thing to do here?” is a human-based question...
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security 4.9: Security built with your workflows in mind
Wikipedia Tells AI Companies to "Stop Scraping"
Google Sues to Disrupt Chinese SMS Phishing Triad
Google is suing more than two dozen unnamed individuals allegedly involved in peddling a popular China-based mobile phishing service that helps scammers impersonate hundreds of trusted brands, blast out text message lures, and convert phished payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google.
In a lawsuit filed in the Southern District of New York on November 12, Google sued to unmask and disrupt 25 “John Doe” defendants allegedly linked to the sale of Lighthouse, a sophisticated phishing kit that makes it simple for even novices to steal payment card data from mobile users. Google said Lighthouse has harmed more than a million victims across 120 countries.
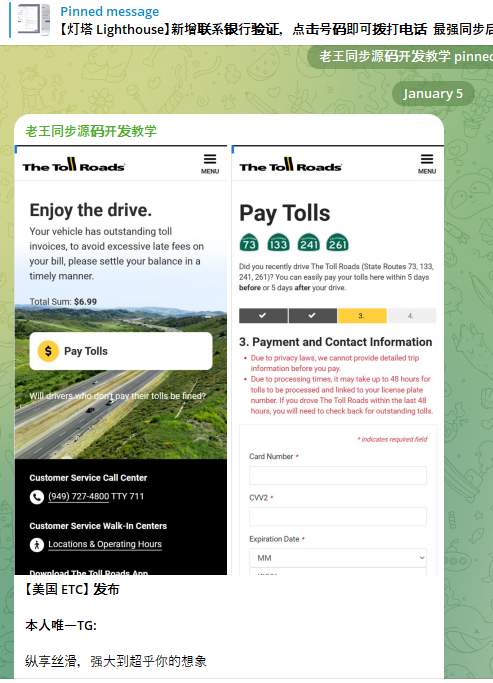
A component of the Chinese phishing kit Lighthouse made to target customers of The Toll Roads, which refers to several state routes through Orange County, Calif.
Lighthouse is one of several prolific phishing-as-a-service operations known as the “Smishing Triad,” and collectively they are responsible for sending millions of text messages that spoof the U.S. Postal Service to supposedly collect some outstanding delivery fee, or that pretend to be a local toll road operator warning of a delinquent toll fee. More recently, Lighthouse has been used to spoof e-commerce websites, financial institutions and brokerage firms.
Regardless of the text message lure used or brand used, the basic scam remains the same: After the visitor enters their payment information, the phishing site will automatically attempt to enroll the card as a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. The phishing site then tells the visitor that their bank is going to verify the transaction by sending a one-time code that needs to be entered into the payment page before the transaction can be completed.
If the recipient provides that one-time code, the scammers can link the victim’s card data to a mobile wallet on a device that they control. Researchers say the fraudsters usually load several stolen wallets onto each mobile device, and wait 7-10 days after that enrollment before selling the phones or using them for fraud.
Google called the scale of the Lighthouse phishing attacks “staggering.” A May 2025 report from Silent Push found the domains used by the Smishing Triad are rotated frequently, with approximately 25,000 phishing domains active during any 8-day period.
Google’s lawsuit alleges the purveyors of Lighthouse violated the company’s trademarks by including Google’s logos on countless phishing websites. The complaint says Lighthouse offers over 600 templates for phishing websites of more than 400 entities, and that Google’s logos were featured on at least a quarter of those templates.
Google is also pursuing Lighthouse under the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act, saying the Lighthouse phishing enterprise encompasses several connected threat actor groups that work together to design and implement complex criminal schemes targeting the general public.
According to Google, those threat actor teams include a “developer group” that supplies the phishing software and templates; a “data broker group” that provides a list of targets; a “spammer group” that provides the tools to send fraudulent text messages in volume; a “theft group,” in charge of monetizing the phished information; and an “administrative group,” which runs their Telegram support channels and discussion groups designed to facilitate collaboration and recruit new members.
“While different members of the Enterprise may play different roles in the Schemes, they all collaborate to execute phishing attacks that rely on the Lighthouse software,” Google’s complaint alleges. “None of the Enterprise’s Schemes can generate revenue without collaboration and cooperation among the members of the Enterprise. All of the threat actor groups are connected to one another through historical and current business ties, including through their use of Lighthouse and the online community supporting its use, which exists on both YouTube and Telegram channels.”
Silent Push’s May report observed that the Smishing Triad boasts it has “300+ front desk staff worldwide” involved in Lighthouse, staff that is mainly used to support various aspects of the group’s fraud and cash-out schemes.
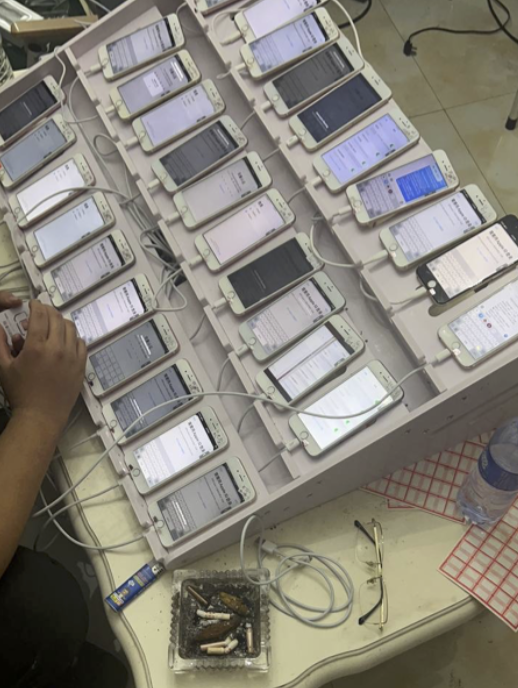

An image shared by an SMS phishing group shows a panel of mobile phones responsible for mass-sending phishing messages. These panels require a live operator because the one-time codes being shared by phishing victims must be used quickly as they generally expire within a few minutes.
Google alleges that in addition to blasting out text messages spoofing known brands, Lighthouse makes it easy for customers to mass-create fake e-commerce websites that are advertised using Google Ads accounts (and paid for with stolen credit cards). These phony merchants collect payment card information at checkout, and then prompt the customer to expect and share a one-time code sent from their financial institution.
Once again, that one-time code is being sent by the bank because the fake e-commerce site has just attempted to enroll the victim’s payment card data in a mobile wallet. By the time a victim understands they will likely never receive the item they just purchased from the fake e-commerce shop, the scammers have already run through hundreds of dollars in fraudulent charges, often at high-end electronics stores or jewelers.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company, and he’s been tracking Chinese SMS phishing groups for several years. Merrill said many Lighthouse customers are now using the phishing kit to erect fake e-commerce websites that are advertised on Google and Meta platforms.
“You find this shop by searching for a particular product online or whatever, and you think you’re getting a good deal,” Merrill said. “But of course you never receive the product, and they will phish that one-time code at checkout.”
Merrill said some of the phishing templates include payment buttons for services like PayPal, and that victims who choose to pay through PayPal can also see their PayPal accounts hijacked.

A fake e-commerce site from the Smishing Triad spoofing PayPal on a mobile device.
“The main advantage of the fake e-commerce site is that it doesn’t require them to send out message lures,” Merrill said, noting that the fake vendor sites have more staying power than traditional phishing sites because it takes far longer for them to be flagged for fraud.
Merrill said Google’s legal action may temporarily disrupt the Lighthouse operators, and could make it easier for U.S. federal authorities to bring criminal charges against the group. But he said the Chinese mobile phishing market is so lucrative right now that it’s difficult to imagine a popular phishing service voluntarily turning out the lights.
Merrill said Google’s lawsuit also can help lay the groundwork for future disruptive actions against Lighthouse and other phishing-as-a-service entities that are operating almost entirely on Chinese networks. According to Silent Push, a majority of the phishing sites created with these kits are sitting at two Chinese hosting companies: Tencent (AS132203) and Alibaba (AS45102).
“Once Google has a default judgment against the Lighthouse guys in court, theoretically they could use that to go to Alibaba and Tencent and say, ‘These guys have been found guilty, here are their domains and IP addresses, we want you to shut these down or we’ll include you in the case.'”
If Google can bring that kind of legal pressure consistently over time, Merrill said, they might succeed in increasing costs for the phishers and more frequently disrupting their operations.
“If you take all of these Chinese phishing kit developers, I have to believe it’s tens of thousands of Chinese-speaking people involved,” he said. “The Lighthouse guys will probably burn down their Telegram channels and disappear for a while. They might call it something else or redevelop their service entirely. But I don’t believe for a minute they’re going to close up shop and leave forever.”
Book Review: The Business of Secrets
The Business of Secrets: Adventures in Selling Encryption Around the World by Fred Kinch (May 24, 2004)
From the vantage point of today, it’s surreal reading about the commercial cryptography business in the 1970s. Nobody knew anything. The manufacturers didn’t know whether the cryptography they sold was any good. The customers didn’t know whether the crypto they bought was any good. Everyone pretended to know, thought they knew, or knew better than to even try to know.
The Business of Secrets is the self-published memoirs of Fred Kinch. He was founder and vice president of—mostly sales—at a US cryptographic hardware company called Datotek, from company’s founding in 1969 until 1982. It’s mostly a disjointed collection of stories about the difficulties of selling to governments worldwide, along with descriptions of the highs and (mostly) lows of foreign airlines, foreign hotels, and foreign travel in general. But it’s also about encryption...