Software Security
Cloudflare Scrubs Aisuru Botnet from Top Domains List
For the past week, domains associated with the massive Aisuru botnet have repeatedly usurped Amazon, Apple, Google and Microsoft in Cloudflare’s public ranking of the most frequently requested websites. Cloudflare responded by redacting Aisuru domain names from their top websites list. The chief executive at Cloudflare says Aisuru’s overlords are using the botnet to boost their malicious domain rankings, while simultaneously attacking the company’s domain name system (DNS) service.
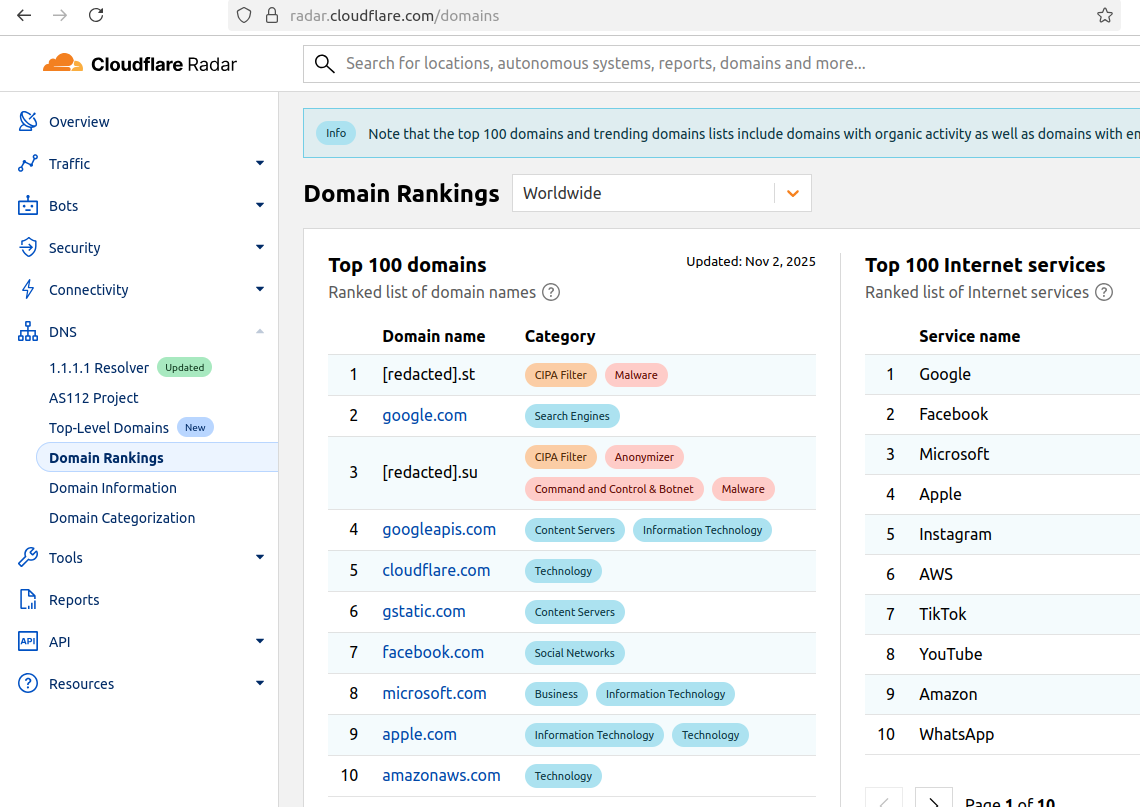
The #1 and #3 positions in this chart are Aisuru botnet controllers with their full domain names redacted. Source: radar.cloudflare.com.
Aisuru is a rapidly growing botnet comprising hundreds of thousands of hacked Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as poorly secured Internet routers and security cameras. The botnet has increased in size and firepower significantly since its debut in 2024, demonstrating the ability to launch record distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks nearing 30 terabits of data per second.
Until recently, Aisuru’s malicious code instructed all infected systems to use DNS servers from Google — specifically, the servers at 8.8.8.8. But in early October, Aisuru switched to invoking Cloudflare’s main DNS server — 1.1.1.1 — and over the past week domains used by Aisuru to control infected systems started populating Cloudflare’s top domain rankings.
As screenshots of Aisuru domains claiming two of the Top 10 positions ping-ponged across social media, many feared this was yet another sign that an already untamable botnet was running completely amok. One Aisuru botnet domain that sat prominently for days at #1 on the list was someone’s street address in Massachusetts followed by “.com”. Other Aisuru domains mimicked those belonging to major cloud providers.
Cloudflare tried to address these security, brand confusion and privacy concerns by partially redacting the malicious domains, and adding a warning at the top of its rankings:
“Note that the top 100 domains and trending domains lists include domains with organic activity as well as domains with emerging malicious behavior.”
Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince told KrebsOnSecurity the company’s domain ranking system is fairly simplistic, and that it merely measures the volume of DNS queries to 1.1.1.1.
“The attacker is just generating a ton of requests, maybe to influence the ranking but also to attack our DNS service,” Prince said, adding that Cloudflare has heard reports of other large public DNS services seeing similar uptick in attacks. “We’re fixing the ranking to make it smarter. And, in the meantime, redacting any sites we classify as malware.”
Renee Burton, vice president of threat intel at the DNS security firm Infoblox, said many people erroneously assumed that the skewed Cloudflare domain rankings meant there were more bot-infected devices than there were regular devices querying sites like Google and Apple and Microsoft.
“Cloudflare’s documentation is clear — they know that when it comes to ranking domains you have to make choices on how to normalize things,” Burton wrote on LinkedIn. “There are many aspects that are simply out of your control. Why is it hard? Because reasons. TTL values, caching, prefetching, architecture, load balancing. Things that have shared control between the domain owner and everything in between.”
Alex Greenland is CEO of the anti-phishing and security firm Epi. Greenland said he understands the technical reason why Aisuru botnet domains are showing up in Cloudflare’s rankings (those rankings are based on DNS query volume, not actual web visits). But he said they’re still not meant to be there.
“It’s a failure on Cloudflare’s part, and reveals a compromise of the trust and integrity of their rankings,” he said.
Greenland said Cloudflare planned for its Domain Rankings to list the most popular domains as used by human users, and it was never meant to be a raw calculation of query frequency or traffic volume going through their 1.1.1.1 DNS resolver.
“They spelled out how their popularity algorithm is designed to reflect real human use and exclude automated traffic (they said they’re good at this),” Greenland wrote on LinkedIn. “So something has evidently gone wrong internally. We should have two rankings: one representing trust and real human use, and another derived from raw DNS volume.”
Why might it be a good idea to wholly separate malicious domains from the list? Greenland notes that Cloudflare Domain Rankings see widespread use for trust and safety determination, by browsers, DNS resolvers, safe browsing APIs and things like TRANCO.
“TRANCO is a respected open source list of the top million domains, and Cloudflare Radar is one of their five data providers,” he continued. “So there can be serious knock-on effects when a malicious domain features in Cloudflare’s top 10/100/1000/million. To many people and systems, the top 10 and 100 are naively considered safe and trusted, even though algorithmically-defined top-N lists will always be somewhat crude.”
Over this past week, Cloudflare started redacting portions of the malicious Aisuru domains from its Top Domains list, leaving only their domain suffix visible. Sometime in the past 24 hours, Cloudflare appears to have begun hiding the malicious Aisuru domains entirely from the web version of that list. However, downloading a spreadsheet of the current Top 200 domains from Cloudflare Radar shows an Aisuru domain still at the very top.
According to Cloudflare’s website, the majority of DNS queries to the top Aisuru domains — nearly 52 percent — originated from the United States. This tracks with my reporting from early October, which found Aisuru was drawing most of its firepower from IoT devices hosted on U.S. Internet providers like AT&T, Comcast and Verizon.
Experts tracking Aisuru say the botnet relies on well more than a hundred control servers, and that for the moment at least most of those domains are registered in the .su top-level domain (TLD). Dot-su is the TLD assigned to the former Soviet Union (.su’s Wikipedia page says the TLD was created just 15 months before the fall of the Berlin wall).
A Cloudflare blog post from October 27 found that .su had the highest “DNS magnitude” of any TLD, referring to a metric estimating the popularity of a TLD based on the number of unique networks querying Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 resolver. The report concluded that the top .su hostnames were associated with a popular online world-building game, and that more than half of the queries for that TLD came from the United States, Brazil and Germany [it’s worth noting that servers for the world-building game Minecraft were some of Aisuru’s most frequent targets].
A simple and crude way to detect Aisuru bot activity on a network may be to set an alert on any systems attempting to contact domains ending in .su. This TLD is frequently abused for cybercrime and by cybercrime forums and services, and blocking access to it entirely is unlikely to raise any legitimate complaints.
Scientists Need a Positive Vision for AI
For many in the research community, it’s gotten harder to be optimistic about the impacts of artificial intelligence.
As authoritarianism is rising around the world, AI-generated “slop” is overwhelming legitimate media, while AI-generated deepfakes are spreading misinformation and parroting extremist messages. AI is making warfare more precise and deadly amidst intransigent conflicts. AI companies are exploiting people in the global South who work as data labelers, and profiting from content creators worldwide by using their work without license or compensation. The industry is also affecting an already-roiling climate with its ...
Cybercriminals Targeting Payroll Sites
Microsoft is warning of a scam involving online payroll systems. Criminals use social engineering to steal people’s credentials, and then divert direct deposits into accounts that they control. Sometimes they do other things to make it harder for the victim to realize what is happening.
I feel like this kind of thing is happening everywhere, with everything. As we move more of our personal and professional lives online, we enable criminals to subvert the very systems we rely on.
AI Summarization Optimization
These days, the most important meeting attendee isn’t a person: It’s the AI notetaker.
This system assigns action items and determines the importance of what is said. If it becomes necessary to revisit the facts of the meeting, its summary is treated as impartial evidence.
But clever meeting attendees can manipulate this system’s record by speaking more to what the underlying AI weights for summarization and importance than to their colleagues. As a result, you can expect some meeting attendees to use language more likely to be captured in summaries, timing their interventions strategically, repeating key points, and employing formulaic phrasing that AI models are more likely to pick up on. Welcome to the world of AI summarization optimization (AISO)...
Alleged Jabber Zeus Coder ‘MrICQ’ in U.S. Custody
A Ukrainian man indicted in 2012 for conspiring with a prolific hacking group to steal tens of millions of dollars from U.S. businesses was arrested in Italy and is now in custody in the United States, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.
Sources close to the investigation say Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov, a 41-year-old from the Russia-controlled city of Donetsk, Ukraine, was previously referenced in U.S. federal charging documents only by his online handle “MrICQ.” According to a 13-year-old indictment (PDF) filed by prosecutors in Nebraska, MrICQ was a developer for a cybercrime group known as “Jabber Zeus.”
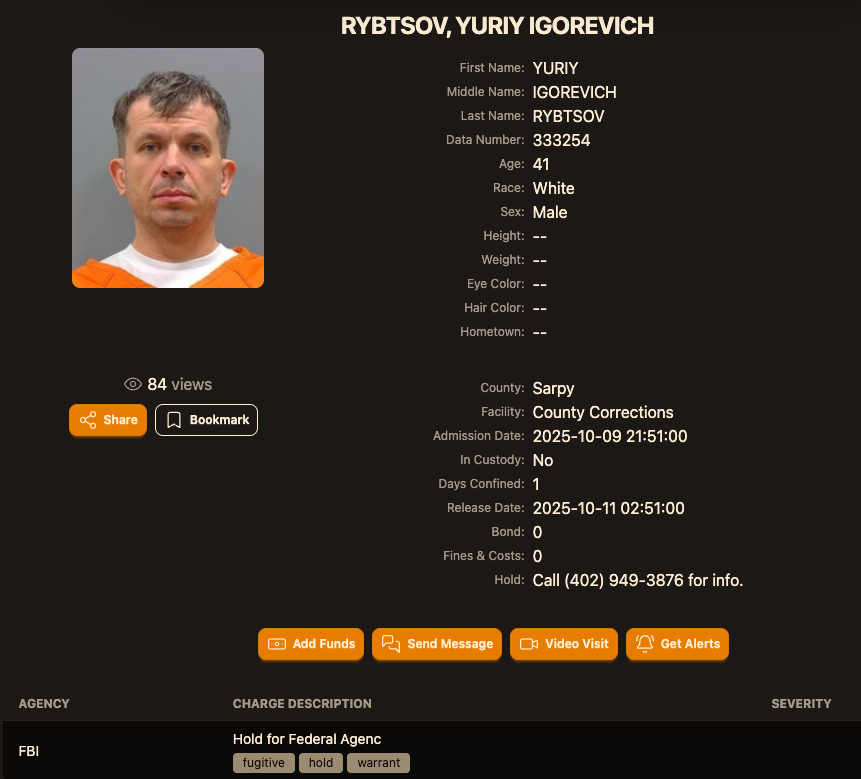
Image: lockedup dot wtf.
The Jabber Zeus name is derived from the malware they used — a custom version of the ZeuS banking trojan — that stole banking login credentials and would send the group a Jabber instant message each time a new victim entered a one-time passcode at a financial institution website. The gang targeted mostly small to mid-sized businesses, and they were an early pioneer of so-called “man-in-the-browser” attacks, malware that can silently intercept any data that victims submit in a web-based form.
Once inside a victim company’s accounts, the Jabber Zeus crew would modify the firm’s payroll to add dozens of “money mules,” people recruited through elaborate work-at-home schemes to handle bank transfers. The mules in turn would forward any stolen payroll deposits — minus their commissions — via wire transfers to other mules in Ukraine and the United Kingdom.
The 2012 indictment targeting the Jabber Zeus crew named MrICQ as “John Doe #3,” and said this person handled incoming notifications of newly compromised victims. The Department of Justice (DOJ) said MrICQ also helped the group launder the proceeds of their heists through electronic currency exchange services.
Two sources familiar with the Jabber Zeus investigation said Rybtsov was arrested in Italy, although the exact date and circumstances of his arrest remain unclear. A summary of recent decisions (PDF) published by the Italian Supreme Court states that in April 2025, Rybtsov lost a final appeal to avoid extradition to the United States.
According to the mugshot website lockedup[.]wtf, Rybtsov arrived in Nebraska on October 9, and was being held under an arrest warrant from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence found breached records from the business profiling site bvdinfo[.]com showing that a 41-year-old Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov worked in a building at 59 Barnaulska St. in Donetsk. Further searching on this address in Constella finds the same apartment building was shared by a business registered to Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, the leader of the Jabber Zeus crew in Ukraine.

Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, seen here performing as “DJ Slava Rich” in Ukraine, in an undated photo from social media.
Penchukov was arrested in 2022 while traveling to meet his wife in Switzerland. Last year, a federal court in Nebraska sentenced Penchukov to 18 years in prison and ordered him to pay more than $73 million in restitution.
Lawrence Baldwin is founder of myNetWatchman, a threat intelligence company based in Georgia that began tracking and disrupting the Jabber Zeus gang in 2009. myNetWatchman had secretly gained access to the Jabber chat server used by the Ukrainian hackers, allowing Baldwin to eavesdrop on the daily conversations between MrICQ and other Jabber Zeus members.
Baldwin shared those real-time chat records with multiple state and federal law enforcement agencies, and with this reporter. Between 2010 and 2013, I spent several hours each day alerting small businesses across the country that their payroll accounts were about to be drained by these cybercriminals.
Those notifications, and Baldwin’s tireless efforts, saved countless would-be victims a great deal of money. In most cases, however, we were already too late. Nevertheless, the pilfered Jabber Zeus group chats provided the basis for dozens of stories published here about small businesses fighting their banks in court over six- and seven-figure financial losses.
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus crew was far ahead of its peers in several respects. For starters, their intercepted chats showed they worked to create a highly customized botnet directly with the author of the original Zeus Trojan — Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev, a Russian man who has long been on the FBI’s “Most Wanted” list. The feds have a standing $3 million reward for information leading to Bogachev’s arrest.

Evgeniy M. Bogachev, in undated photos.
The core innovation of Jabber Zeus was an alert that MrICQ would receive each time a new victim entered a one-time password code into a phishing page mimicking their financial institution. The gang’s internal name for this component was “Leprechaun,” (the video below from myNetWatchman shows it in action). Jabber Zeus would actually re-write the HTML code as displayed in the victim’s browser, allowing them to intercept any passcodes sent by the victim’s bank for multi-factor authentication.
“These guys had compromised such a large number of victims that they were getting buried in a tsunami of stolen banking credentials,” Baldwin told KrebsOnSecurity. “But the whole point of Leprechaun was to isolate the highest-value credentials — the commercial bank accounts with two-factor authentication turned on. They knew these were far juicier targets because they clearly had a lot more money to protect.”
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus trojan also included a custom “backconnect” component that allowed the hackers to relay their bank account takeovers through the victim’s own infected PC.
“The Jabber Zeus crew were literally connecting to the victim’s bank account from the victim’s IP address, or from the remote control function and by fully emulating the device,” he said. “That trojan was like a hot knife through butter of what everyone thought was state-of-the-art secure online banking at the time.”
Although the Jabber Zeus crew was in direct contact with the Zeus author, the chats intercepted by myNetWatchman show Bogachev frequently ignored the group’s pleas for help. The government says the real leader of the Jabber Zeus crew was Maksim Yakubets, a 38-year Ukrainian man with Russian citizenship who went by the hacker handle “Aqua.”

Alleged Evil Corp leader Maksim “Aqua” Yakubets. Image: FBI
The Jabber chats intercepted by Baldwin show that Aqua interacted almost daily with MrICQ, Tank and other members of the hacking team, often facilitating the group’s money mule and cashout activities remotely from Russia.
The government says Yakubets/Aqua would later emerge as the leader of an elite cybercrime ring of at least 17 hackers that referred to themselves internally as “Evil Corp.” Members of Evil Corp developed and used the Dridex (a.k.a. Bugat) trojan, which helped them siphon more than $100 million from hundreds of victim companies in the United States and Europe.
This 2019 story about the government’s $5 million bounty for information leading to Yakubets’s arrest includes excerpts of conversations between Aqua, Tank, Bogachev and other Jabber Zeus crew members discussing stories I’d written about their victims. Both Baldwin and I were interviewed at length for a new weekly six-part podcast by the BBC that delves deep into the history of Evil Corp. Episode One focuses on the evolution of Zeus, while the second episode centers on an investigation into the group by former FBI agent Jim Craig.

Image: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/w3ct89y8
Friday Squid Blogging: Giant Squid at the Smithsonian
I can’t believe that I haven’t yet posted this picture of a giant squid at the Smithsonian.
As usual, you can also use this squid post to talk about the security stories in the news that I haven’t covered.
Will AI Strengthen or Undermine Democracy?
Listen to the Audio on NextBigIdeaClub.com
Below, co-authors Bruce Schneier and Nathan E. Sanders share five key insights from their new book, Rewiring Democracy: How AI Will Transform Our Politics, Government, and Citizenship.
What’s the big idea?
AI can be used both for and against the public interest within democracies. It is already being used in the governing of nations around the world, and there is no escaping its continued use in the future by leaders, policy makers, and legal enforcers. How we wire AI into democracy today will determine if it becomes a tool of oppression or empowerment...
The AI-Designed Bioweapon Arms Race
Interesting article about the arms race between AI systems that invent/design new biological pathogens, and AI systems that detect them before they’re created:
The team started with a basic test: use AI tools to design variants of the toxin ricin, then test them against the software that is used to screen DNA orders. The results of the test suggested there was a risk of dangerous protein variants slipping past existing screening software, so the situation was treated like the equivalent of a zero-day vulnerability.
[…]
Details of that original test are ...
Signal’s Post-Quantum Cryptographic Implementation
Signal has just rolled out its quantum-safe cryptographic implementation.
Ars Technica has a really good article with details:
Ultimately, the architects settled on a creative solution. Rather than bolt KEM onto the existing double ratchet, they allowed it to remain more or less the same as it had been. Then they used the new quantum-safe ratchet to implement a parallel secure messaging system.
Now, when the protocol encrypts a message, it sources encryption keys from both the classic Double Ratchet and the new ratchet. It then mixes the two keys together (using a cryptographic key derivation function) to get a new encryption key that has all of the security of the classical Double Ratchet but now has quantum security, too...
Aisuru Botnet Shifts from DDoS to Residential Proxies
Aisuru, the botnet responsible for a series of record-smashing distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks this year, recently was overhauled to support a more low-key, lucrative and sustainable business: Renting hundreds of thousands of infected Internet of Things (IoT) devices to proxy services that help cybercriminals anonymize their traffic. Experts say a glut of proxies from Aisuru and other sources is fueling large-scale data harvesting efforts tied to various artificial intelligence (AI) projects, helping content scrapers evade detection by routing their traffic through residential connections that appear to be regular Internet users.
First identified in August 2024, Aisuru has spread to at least 700,000 IoT systems, such as poorly secured Internet routers and security cameras. Aisuru’s overlords have used their massive botnet to clobber targets with headline-grabbing DDoS attacks, flooding targeted hosts with blasts of junk requests from all infected systems simultaneously.
In June, Aisuru hit KrebsOnSecurity.com with a DDoS clocking at 6.3 terabits per second — the biggest attack that Google had ever mitigated at the time. In the weeks and months that followed, Aisuru’s operators demonstrated DDoS capabilities of nearly 30 terabits of data per second — well beyond the attack mitigation capabilities of most Internet destinations.
These digital sieges have been particularly disruptive this year for U.S.-based Internet service providers (ISPs), in part because Aisuru recently succeeded in taking over a large number of IoT devices in the United States. And when Aisuru launches attacks, the volume of outgoing traffic from infected systems on these ISPs is often so high that it can disrupt or degrade Internet service for adjacent (non-botted) customers of the ISPs.
“Multiple broadband access network operators have experienced significant operational impact due to outbound DDoS attacks in excess of 1.5Tb/sec launched from Aisuru botnet nodes residing on end-customer premises,” wrote Roland Dobbins, principal engineer at Netscout, in a recent executive summary on Aisuru. “Outbound/crossbound attack traffic exceeding 1Tb/sec from compromised customer premise equipment (CPE) devices has caused significant disruption to wireline and wireless broadband access networks. High-throughput attacks have caused chassis-based router line card failures.”
The incessant attacks from Aisuru have caught the attention of federal authorities in the United States and Europe (many of Aisuru’s victims are customers of ISPs and hosting providers based in Europe). Quite recently, some of the world’s largest ISPs have started informally sharing block lists identifying the rapidly shifting locations of the servers that the attackers use to control the activities of the botnet.
Experts say the Aisuru botmasters recently updated their malware so that compromised devices can more easily be rented to so-called “residential proxy” providers. These proxy services allow paying customers to route their Internet communications through someone else’s device, providing anonymity and the ability to appear as a regular Internet user in almost any major city worldwide.
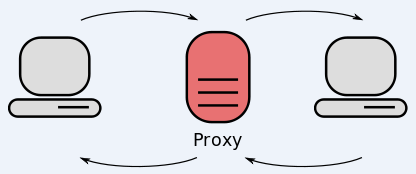
From a website’s perspective, the IP traffic of a residential proxy network user appears to originate from the rented residential IP address, not from the proxy service customer. Proxy services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence. But they are massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity (think advertising fraud, credential stuffing) because they can make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source.
And as we’ll see in a moment, this entire shadowy industry appears to be shifting its focus toward enabling aggressive content scraping activity that continuously feeds raw data into large language models (LLMs) built to support various AI projects.
‘INSANE’ GROWTH
Riley Kilmer is co-founder of spur.us, a service that tracks proxy networks. Kilmer said all of the top proxy services have grown exponentially over the past six months — with some adding between 10 to 200 times more proxies for rent.
“I just checked, and in the last 90 days we’ve seen 250 million unique residential proxy IPs,” Kilmer said. “That is insane. That is so high of a number, it’s unheard of. These proxies are absolutely everywhere now.”
To put Kilmer’s comments in perspective, here was Spur’s view of the Top 10 proxy networks by approximate install base, circa May 2025:
AUPROXIES_PROXY 66,097
RAYOBYTE_PROXY 43,894
OXYLABS_PROXY 43,008
WEBSHARE_PROXY 39,800
IPROYAL_PROXY 32,723
PROXYCHEAP_PROXY 26,368
IPIDEA_PROXY 26,202
MYPRIVATEPROXY_PROXY 25,287
HYPE_PROXY 18,185
MASSIVE_PROXY 17,152
Today, Spur says it is tracking an unprecedented spike in available proxies across all providers, including;
LUMINATI_PROXY 11,856,421
NETNUT_PROXY 10,982,458
ABCPROXY_PROXY 9,294,419
OXYLABS_PROXY 6,754,790
IPIDEA_PROXY 3,209,313
EARNFM_PROXY 2,659,913
NODEMAVEN_PROXY 2,627,851
INFATICA_PROXY 2,335,194
IPROYAL_PROXY 2,032,027
YILU_PROXY 1,549,155
Reached for comment about the apparent rapid growth in their proxy network, Oxylabs (#4 on Spur’s list) said while their proxy pool did grow recently, it did so at nowhere near the rate cited by Spur.
“We don’t systematically track other providers’ figures, and we’re not aware of any instances of 10× or 100× growth, especially when it comes to a few bigger companies that are legitimate businesses,” the company said in a written statement.
Bright Data was formerly known as Luminati Networks, the name that is currently at the top of Spur’s list of the biggest residential proxy networks, with more than 11 million proxies. Bright Data likewise told KrebsOnSecurity that Spur’s current estimates of its proxy network are dramatically overstated and inaccurate.
“We did not actively initiate nor do we see any 10x or 100x expansion of our network, which leads me to believe that someone might be presenting these IPs as Bright Data’s in some way,” said Rony Shalit, Bright Data’s chief compliance and ethics officer. “In many cases in the past, due to us being the leading data collection proxy provider, IPs were falsely tagged as being part of our network, or while being used by other proxy providers for malicious activity.”
“Our network is only sourced from verified IP providers and a robust opt-in only residential peers, which we work hard and in complete transparency to obtain,” Shalit continued. “Every DC, ISP or SDK partner is reviewed and approved, and every residential peer must actively opt in to be part of our network.”
HK NETWORK
Even Spur acknowledges that Luminati and Oxylabs are unlike most other proxy services on their top proxy providers list, in that these providers actually adhere to “know-your-customer” policies, such as requiring video calls with all customers, and strictly blocking customers from reselling access.
Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks. Brundage said if there is increasing confusion around which proxy networks are the most worrisome, it’s because nearly all of these lesser-known proxy services have evolved into highly incestuous bandwidth resellers. What’s more, he said, some proxy providers do not appreciate being tracked and have been known to take aggressive steps to confuse systems that scan the Internet for residential proxy nodes.
Brundage said most proxy services today have created their own software development kit or SDK that other app developers can bundle with their code to earn revenue. These SDKs quietly modify the user’s device so that some portion of their bandwidth can be used to forward traffic from proxy service customers.
“Proxy providers have pools of constantly churning IP addresses,” he said. “These IP addresses are sourced through various means, such as bandwidth-sharing apps, botnets, Android SDKs, and more. These providers will often either directly approach resellers or offer a reseller program that allows users to resell bandwidth through their platform.”
Many SDK providers say they require full consent before allowing their software to be installed on end-user devices. Still, those opt-in agreements and consent checkboxes may be little more than a formality for cybercriminals like the Aisuru botmasters, who can earn a commission each time one of their infected devices is forced to install some SDK that enables one or more of these proxy services.
Depending on its structure, a single provider may operate hundreds of different proxy pools at a time — all maintained through other means, Brundage said.
“Often, you’ll see resellers maintaining their own proxy pool in addition to an upstream provider,” he said. “It allows them to market a proxy pool to high-value clients and offer an unlimited bandwidth plan for cheap reduce their own costs.”
Some proxy providers appear to be directly in league with botmasters. Brundage identified one proxy provider that was aggressively advertising cheap and plentiful bandwidth to content scraping companies. After scanning that provider’s pool of available proxies, Brundage said he found a one-to-one match with IP addresses he’d previously mapped to the Aisuru botnet.
Brundage says that by almost any measurement, the world’s largest residential proxy service is IPidea, a China-based proxy network. IPidea is #5 on Spur’s Top 10, and Brundage said its brands include ABCProxy (#3), Roxlabs, LunaProxy, PIA S5 Proxy, PyProxy, 922Proxy, 360Proxy, IP2World, and Cherry Proxy. Spur’s Kilmer said they also track Yilu Proxy (#10) as IPidea.
Brundage said all of these providers operate under a corporate umbrella known on the cybercrime forums as “HK Network.”
“The way it works is there’s this whole reseller ecosystem, where IPidea will be incredibly aggressive and approach all these proxy providers with the offer, ‘Hey, if you guys buy bandwidth from us, we’ll give you these amazing reseller prices,'” Brundage explained. “But they’re also very aggressive in recruiting resellers for their apps.”
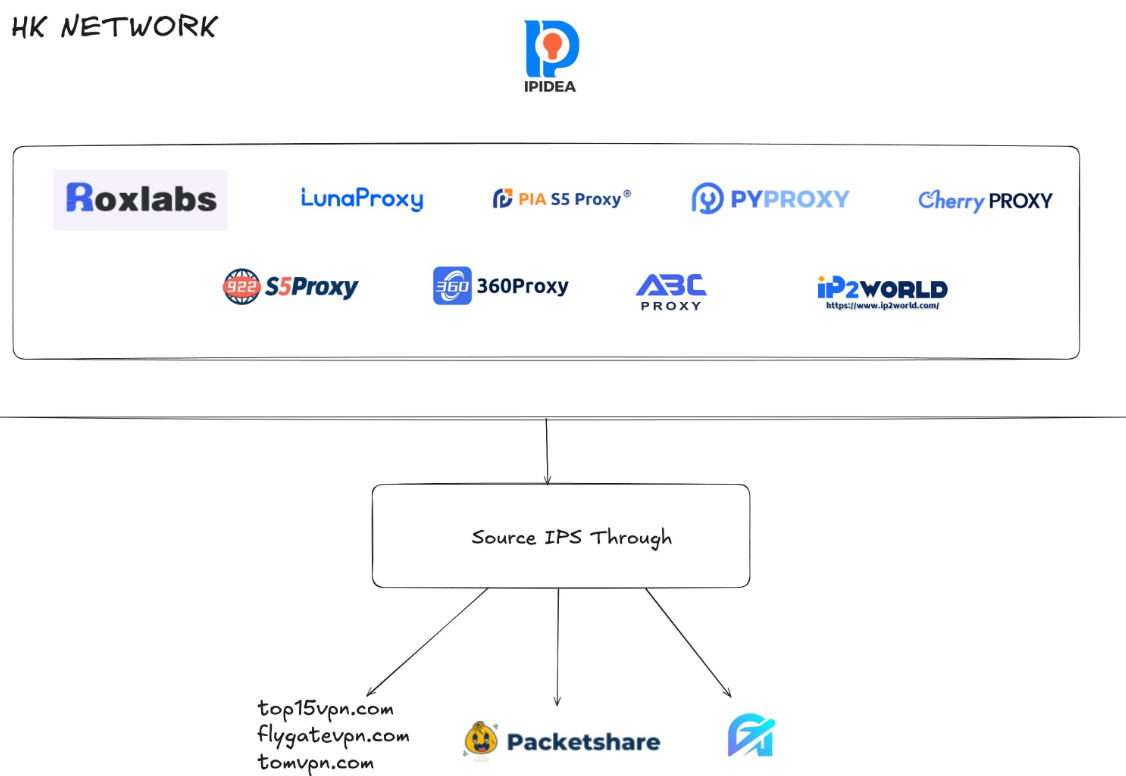
A graphic depicting the relationship between proxy providers that Synthient found are white labeling IPidea proxies. Image: Synthient.com.
Those apps include a range of low-cost and “free” virtual private networking (VPN) services that indeed allow users to enjoy a free VPN, but which also turn the user’s device into a traffic relay that can be rented to cybercriminals, or else parceled out to countless other proxy networks.
“They have all this bandwidth to offload,” Brundage said of IPidea and its sister networks. “And they can do it through their own platforms, or they go get resellers to do it for them by advertising on sketchy hacker forums to reach more people.”
One of IPidea’s core brands is 922S5Proxy, which is a not-so-subtle nod to the 911S5Proxy service that was hugely popular between 2015 and 2022. In July 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive into 911S5Proxy’s origins and apparent owners in China. Less than a week later, 911S5Proxy announced it was closing down after the company’s servers were massively hacked.
That 2022 story named Yunhe Wang from Beijing as the apparent owner and/or manager of the 911S5 proxy service. In May 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice arrested Mr Wang, alleging that his network was used to steal billions of dollars from financial institutions, credit card issuers, and federal lending programs. At the same time, the U.S. Treasury Department announced sanctions against Wang and two other Chinese nationals for operating 911S5Proxy.
The website for 922Proxy.
DATA SCRAPING FOR AI
In recent months, multiple experts who track botnet and proxy activity have shared that a great deal of content scraping which ultimate benefits AI companies is now leveraging these proxy networks to further obfuscate their aggressive data-slurping activity. That’s because by routing it through residential IP addresses, content scraping firms can make their traffic far trickier to filter out.
“It’s really difficult to block, because there’s a risk of blocking real people,” Spur’s Kilmer said of the LLM scraping activity that is fed through individual residential IP addresses, which are often shared by multiple customers at once.
Kilmer says the AI industry has brought a veneer of legitimacy to residential proxy business, which has heretofore mostly been associated with sketchy affiliate money making programs, automated abuse, and unwanted Internet traffic.
“Web crawling and scraping has always been a thing, but AI made it like a commodity, data that had to be collected,” Kilmer said. “Everybody wanted to monetize their own data pots, and how they monetize that is different across the board.”
Kilmer said many LLM-related scrapers rely on residential proxies in cases where the content provider has restricted access to their platform in some way, such as forcing interaction through an app, or keeping all content behind a login page with multi-factor authentication.
“Where the cost of data is out of reach — there is some exclusivity or reason they can’t access the data — they’ll turn to residential proxies so they look like a real person accessing that data,” Kilmer said of the content scraping efforts.
Aggressive AI crawlers increasingly are overloading community-maintained infrastructure, causing what amounts to persistent DDoS attacks on vital public resources. A report earlier this year from LibreNews found some open-source projects now see as much as 97 percent of their traffic originating from AI company bots, dramatically increasing bandwidth costs, service instability, and burdening already stretched-thin maintainers.
Cloudflare is now experimenting with tools that will allow content creators to charge a fee to AI crawlers to scrape their websites. The company’s “pay-per-crawl” feature is currently in a private beta, but it lets publishers set their own prices that bots must pay before scraping content.
On October 22, the social media and news network Reddit sued Oxylabs (PDF) and several other proxy providers, alleging that their systems enabled the mass-scraping of Reddit user content even though Reddit had taken steps to block such activity.
“Recognizing that Reddit denies scrapers like them access to its site, Defendants scrape the data from Google’s search results instead,” the lawsuit alleges. “They do so by masking their identities, hiding their locations, and disguising their web scrapers as regular people (among other techniques) to circumvent or bypass the security restrictions meant to stop them.”
Denas Grybauskas, chief governance and strategy officer at Oxylabs, said the company was shocked and disappointed by the lawsuit.
“Reddit has made no attempt to speak with us directly or communicate any potential concerns,” Grybauskas said in a written statement. “Oxylabs has always been and will continue to be a pioneer and an industry leader in public data collection, and it will not hesitate to defend itself against these allegations. Oxylabs’ position is that no company should claim ownership of public data that does not belong to them. It is possible that it is just an attempt to sell the same public data at an inflated price.”
As big and powerful as Aisuru may be, it is hardly the only botnet that is contributing to the overall broad availability of residential proxies. For example, on June 5 the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center warned that an IoT malware threat dubbed BADBOX 2.0 had compromised millions of smart-TV boxes, digital projectors, vehicle infotainment units, picture frames, and other IoT devices.
In July 2025, Google filed a lawsuit in New York federal court against the Badbox botnet’s alleged perpetrators. Google said the Badbox 2.0 botnet “compromised more than 10 million uncertified devices running Android’s open-source software, which lacks Google’s security protections. Cybercriminals infected these devices with pre-installed malware and exploited them to conduct large-scale ad fraud and other digital crimes.”
A FAMILIAR DOMAIN NAME
Brundage said the Aisuru botmasters have their own SDK, and for some reason part of its code tells many newly-infected systems to query the domain name fuckbriankrebs[.]com. This may be little more than an elaborate “screw you” to this site’s author: One of the botnet’s alleged partners goes by the handle “Forky,” and was identified in June by KrebsOnSecurity as a young man from Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Brundage noted that only systems infected with Aisuru’s Android SDK will be forced to resolve the domain. Initially, there was some discussion about whether the domain might have some utility as a “kill switch” capable of disrupting the botnet’s operations, although Brundage and others interviewed for this story say that is unlikely.
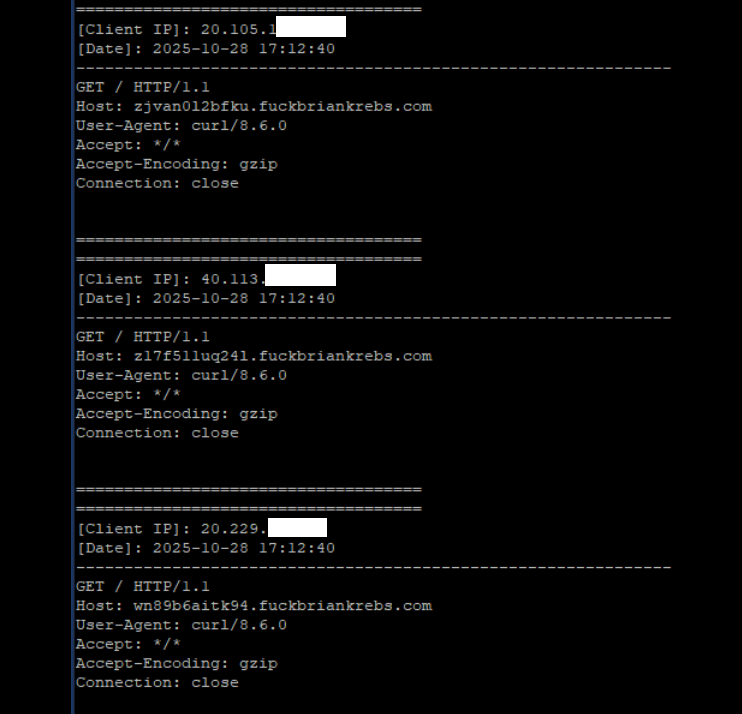
A tiny sample of the traffic after a DNS server was enabled on the newly registered domain fuckbriankrebs dot com. Each unique IP address requested its own unique subdomain. Image: Seralys.
For one thing, they said, if the domain was somehow critical to the operation of the botnet, why was it still unregistered and actively for-sale? Why indeed, we asked. Happily, the domain name was deftly snatched up last week by Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” for the security intelligence company Seralys.
Caturegli enabled a passive DNS server on that domain and within a few hours received more than 700,000 requests for unique subdomains on fuckbriankrebs[.]com.
But even with that visibility into Aisuru, it is difficult to use this domain check-in feature to measure its true size, Brundage said. After all, he said, the systems that are phoning home to the domain are only a small portion of the overall botnet.
“The bots are hardcoded to just spam lookups on the subdomains,” he said. “So anytime an infection occurs or it runs in the background, it will do one of those DNS queries.”

Caturegli briefly configured all subdomains on fuckbriankrebs dot com to display this ASCII art image to visiting systems today.
The domain fuckbriankrebs[.]com has a storied history. On its initial launch in 2009, it was used to spread malicious software by the Cutwail spam botnet. In 2011, the domain was involved in a notable DDoS against this website from a botnet powered by Russkill (a.k.a. “Dirt Jumper”).
Domaintools.com finds that in 2015, fuckbriankrebs[.]com was registered to an email address attributed to David “Abdilo” Crees, a 27-year-old Australian man sentenced in May 2025 to time served for cybercrime convictions related to the Lizard Squad hacking group.
Social Engineering People’s Credit Card Details
Good Wall Street Journal article on criminal gangs that scam people out of their credit card information:
Your highway toll payment is now past due, one text warns. You have U.S. Postal Service fees to pay, another threatens. You owe the New York City Department of Finance for unpaid traffic violations.
The texts are ploys to get unsuspecting victims to fork over their credit-card details. The gangs behind the scams take advantage of this information to buy iPhones, gift cards, clothing and cosmetics.
Criminal organizations operating out of China, which investigators blame for the toll and postage messages, have used them to make more than $1 billion over the last three years, according to the Department of Homeland Security...
Introducing Red Hat’s STIG-hardened UBI for NVIDIA GPUs on Red Hat OpenShift
Increasing the accessibility of managed security services
Louvre Jewel Heist
I assume I don’t have to explain last week’s Louvre jewel heist. I love a good caper, and have (like many others) eagerly followed the details. An electric ladder to a second-floor window, an angle grinder to get into the room and the display cases, security guards there more to protect patrons than valuables—seven minutes, in and out.
There were security lapses:
The Louvre, it turns out—at least certain nooks of the ancient former palace—is something like an anopticon: a place where no one is observed. The world now knows what the four thieves (two burglars and two accomplices) realized as recently as last week: The museum’s Apollo Gallery, which housed the stolen items, was monitored by a single outdoor camera angled away from its only exterior point of entry, a balcony. In other words, a free-roaming Roomba could have provided the world’s most famous museum with more information about the interior of this space. There is no surveillance footage of the break-in...
First Wap: A Surveillance Computer You’ve Never Heard Of
Mother Jones has a long article on surveillance arms manufacturers, their wares, and how they avoid export control laws:
Operating from their base in Jakarta, where permissive export laws have allowed their surveillance business to flourish, First Wap’s European founders and executives have quietly built a phone-tracking empire, with a footprint extending from the Vatican to the Middle East to Silicon Valley.
It calls its proprietary system Altamides, which it describes in promotional materials as “a unified platform to covertly locate the whereabouts of single or multiple suspects in real-time, to detect movement patterns, and to detect whether suspects are in close vicinity with each other.”...
Friday Squid Blogging: “El Pulpo The Squid”
There is a new cigar named “El Pulpo The Squid.” Yes, that means “The Octopus The Squid.”
As usual, you can also use this squid post to talk about the security stories in the news that I haven’t covered.
Part Four of The Kryptos Sculpture
Two people found the solution. They used the power of research, not cryptanalysis, finding clues amongst the Sanborn papers at the Smithsonian’s Archives of American Art.
This comes as an awkward time, as Sanborn is auctioning off the solution. There were legal threats—I don’t understand their basis—and the solvers are not publishing their solution.
Serious F5 Breach
This is bad:
F5, a Seattle-based maker of networking software, disclosed the breach on Wednesday. F5 said a “sophisticated” threat group working for an undisclosed nation-state government had surreptitiously and persistently dwelled in its network over a “long-term.” Security researchers who have responded to similar intrusions in the past took the language to mean the hackers were inside the F5 network for years.
During that time, F5 said, the hackers took control of the network segment the company uses to create and distribute updates for BIG IP, a line of server appliances that F5 ...
Canada Fines Cybercrime Friendly Cryptomus $176M
Financial regulators in Canada this week levied $176 million in fines against Cryptomus, a digital payments platform that supports dozens of Russian cryptocurrency exchanges and websites hawking cybercrime services. The penalties for violating Canada’s anti money-laundering laws come ten months after KrebsOnSecurity noted that Cryptomus’s Vancouver street address was home to dozens of foreign currency dealers, money transfer businesses, and cryptocurrency exchanges — none of which were physically located there.

On October 16, the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Center of Canada (FINTRAC) imposed a $176,960,190 penalty on Xeltox Enterprises Ltd., more commonly known as the cryptocurrency payments platform Cryptomus.
FINTRAC found that Cryptomus failed to submit suspicious transaction reports in cases where there were reasonable grounds to suspect that they were related to the laundering of proceeds connected to trafficking in child sexual abuse material, fraud, ransomware payments and sanctions evasion.
“Given that numerous violations in this case were connected to trafficking in child sexual abuse material, fraud, ransomware payments and sanctions evasion, FINTRAC was compelled to take this unprecedented enforcement action,” said Sarah Paquet, director and CEO at the regulatory agency.
In December 2024, KrebsOnSecurity covered research by blockchain analyst and investigator Richard Sanders, who’d spent several months signing up for various cybercrime services, and then tracking where their customer funds go from there. The 122 services targeted in Sanders’s research all used Cryptomus, and included some of the more prominent businesses advertising on the cybercrime forums, such as:
-abuse-friendly or “bulletproof” hosting providers like anonvm[.]wtf, and PQHosting;
-sites selling aged email, financial, or social media accounts, such as verif[.]work and kopeechka[.]store;
-anonymity or “proxy” providers like crazyrdp[.]com and rdp[.]monster;
-anonymous SMS services, including anonsim[.]net and smsboss[.]pro.
Flymoney, one of dozens of cryptocurrency exchanges apparently nested at Cryptomus. The image from this website has been machine translated from Russian.
Sanders found at least 56 cryptocurrency exchanges were using Cryptomus to process transactions, including financial entities with names like casher[.]su, grumbot[.]com, flymoney[.]biz, obama[.]ru and swop[.]is.
“These platforms were built for Russian speakers, and they each advertised the ability to anonymously swap one form of cryptocurrency for another,” the December 2024 story noted. “They also allowed the exchange of cryptocurrency for cash in accounts at some of Russia’s largest banks — nearly all of which are currently sanctioned by the United States and other western nations.”
Reached for comment on FINTRAC’s action, Sanders told KrebsOnSecurity he was surprised it took them so long.
“I have no idea why they don’t just sanction them or prosecute them,” Sanders said. “I’m not let down with the fine amount but it’s also just going to be the cost of doing business to them.”
The $173 million fine is a significant sum for FINTRAC, which imposed 23 such penalties last year totaling less than $26 million. But Sanders says FINTRAC still has much work to do in pursuing other shadowy money service businesses (MSBs) that are registered in Canada but are likely money laundering fronts for entities based in Russia and Iran.

In an investigation published in July 2024, CTV National News and the Investigative Journalism Foundation (IJF) documented dozens of cases across Canada where multiple MSBs are incorporated at the same address, often without the knowledge or consent of the location’s actual occupant.
Their inquiry found that the street address for Cryptomus parent Xeltox Enterprises was listed as the home of at least 76 foreign currency dealers, eight MSBs, and six cryptocurrency exchanges. At that address is a three-story building that used to be a bank and now houses a massage therapy clinic and a co-working space. But the news outlets found none of the MSBs or currency dealers were paying for services at that co-working space.
The reporters also found another collection of 97 MSBs clustered at an address for a commercial office suite in Ontario, even though there was no evidence any of these companies had ever arranged for any business services at that address.
Failures in Face Recognition
Interesting article on people with nonstandard faces and how facial recognition systems fail for them.
Some of those living with facial differences tell WIRED they have undergone multiple surgeries and experienced stigma for their entire lives, which is now being echoed by the technology they are forced to interact with. They say they haven’t been able to access public services due to facial verification services failing, while others have struggled to access financial services. Social media filters and face-unlocking systems on phones often won’t work, they say...