Software Security
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, November 2025 Edition
Microsoft this week pushed security updates to fix more than 60 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and supported software, including at least one zero-day bug that is already being exploited. Microsoft also fixed a glitch that prevented some Windows 10 users from taking advantage of an extra year of security updates, which is nice because the zero-day flaw and other critical weaknesses affect all versions of Windows, including Windows 10.

Affected products this month include the Windows OS, Office, SharePoint, SQL Server, Visual Studio, GitHub Copilot, and Azure Monitor Agent. The zero-day threat concerns a memory corruption bug deep in the Windows innards called CVE-2025-62215. Despite the flaw’s zero-day status, Microsoft has assigned it an “important” rating rather than critical, because exploiting it requires an attacker to already have access to the target’s device.
“These types of vulnerabilities are often exploited as part of a more complex attack chain,” said Johannes Ullrich, dean of research for the SANS Technology Institute. “However, exploiting this specific vulnerability is likely to be relatively straightforward, given the existence of prior similar vulnerabilities.”
Ben McCarthy, lead cybersecurity engineer at Immersive, called attention to CVE-2025-60274, a critical weakness in a core Windows graphic component (GDI+) that is used by a massive number of applications, including Microsoft Office, web servers processing images, and countless third-party applications.
“The patch for this should be an organization’s highest priority,” McCarthy said. “While Microsoft assesses this as ‘Exploitation Less Likely,’ a 9.8-rated flaw in a ubiquitous library like GDI+ is a critical risk.”
Microsoft patched a critical bug in Office — CVE-2025-62199 — that can lead to remote code execution on a Windows system. Alex Vovk, CEO and co-founder of Action1, said this Office flaw is a high priority because it is low complexity, needs no privileges, and can be exploited just by viewing a booby-trapped message in the Preview Pane.
Many of the more concerning bugs addressed by Microsoft this month affect Windows 10, an operating system that Microsoft officially ceased supporting with patches last month. As that deadline rolled around, however, Microsoft began offering Windows 10 users an extra year of free updates, so long as they register their PC to an active Microsoft account.
Judging from the comments on last month’s Patch Tuesday post, that registration worked for a lot of Windows 10 users, but some readers reported the option for an extra year of updates was never offered. Nick Carroll, cyber incident response manager at Nightwing, notes that Microsoft has recently released an out-of-band update to address issues when trying to enroll in the Windows 10 Consumer Extended Security Update program.
“If you plan to participate in the program, make sure you update and install KB5071959 to address the enrollment issues,” Carroll said. “After that is installed, users should be able to install other updates such as today’s KB5068781 which is the latest update to Windows 10.”
Chris Goettl at Ivanti notes that in addition to Microsoft updates today, third-party updates from Adobe and Mozilla have already been released. Also, an update for Google Chrome is expected soon, which means Edge will also be in need of its own update.
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a clickable breakdown of each individual fix from Microsoft, indexed by severity and CVSS score. Enterprise Windows admins involved in testing patches before rolling them out should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the skinny on any updates gone awry.
As always, please don’t neglect to back up your data (if not your entire system) at regular intervals, and feel free to sound off in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these fixes.
[Author’s note: This post was intended to appear on the homepage on Tuesday, Nov. 11. I’m still not sure how it happened, but somehow this story failed to publish that day. My apologies for the oversight.]
Friday Squid Blogging: Pilot Whales Eat a Lot of Squid
Short-finned pilot wales (Globicephala macrorhynchus) eat at lot of squid:
To figure out a short-finned pilot whale’s caloric intake, Gough says, the team had to combine data from a variety of sources, including movement data from short-lasting tags, daily feeding rates from satellite tags, body measurements collected via aerial drones, and sifting through the stomachs of unfortunate whales that ended up stranded on land.
Once the team pulled all this data together, they estimated that a typical whale will eat between 82 and 202 squid a day. To meet their energy needs, a whale will have to consume an average of 140 squid a day. Annually, that’s about 74,000 squid per whale. For all the whales in the area, that amounts to about 88,000 tons of squid eaten every year...
Upcoming Speaking Engagements
This is a current list of where and when I am scheduled to speak:
- My coauthor Nathan E. Sanders and I are speaking at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington, DC at noon ET on November 17, 2025. The event is hosted by the POPVOX Foundation and the topic is “AI and Congress: Practical Steps to Govern and Prepare.”
- I’m speaking on “Integrity and Trustworthy AI” at North Hennepin Community College in Brooklyn Park, Minnesota, USA, on Friday, November 21, 2025, at 2:00 PM CT. The event is cohosted by the college and The Twin Cities IEEE Computer Society...
The Role of Humans in an AI-Powered World
As AI capabilities grow, we must delineate the roles that should remain exclusively human. The line seems to be between fact-based decisions and judgment-based decisions.
For example, in a medical context, if an AI was demonstrably better at reading a test result and diagnosing cancer than a human, you would take the AI in a second. You want the more accurate tool. But justice is harder because justice is inherently a human quality in a way that “Is this tumor cancerous?” is not. That’s a fact-based question. “What’s the right thing to do here?” is a human-based question...
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security 4.9: Security built with your workflows in mind
Wikipedia Tells AI Companies to "Stop Scraping"
Google Sues to Disrupt Chinese SMS Phishing Triad
Google is suing more than two dozen unnamed individuals allegedly involved in peddling a popular China-based mobile phishing service that helps scammers impersonate hundreds of trusted brands, blast out text message lures, and convert phished payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google.
In a lawsuit filed in the Southern District of New York on November 12, Google sued to unmask and disrupt 25 “John Doe” defendants allegedly linked to the sale of Lighthouse, a sophisticated phishing kit that makes it simple for even novices to steal payment card data from mobile users. Google said Lighthouse has harmed more than a million victims across 120 countries.
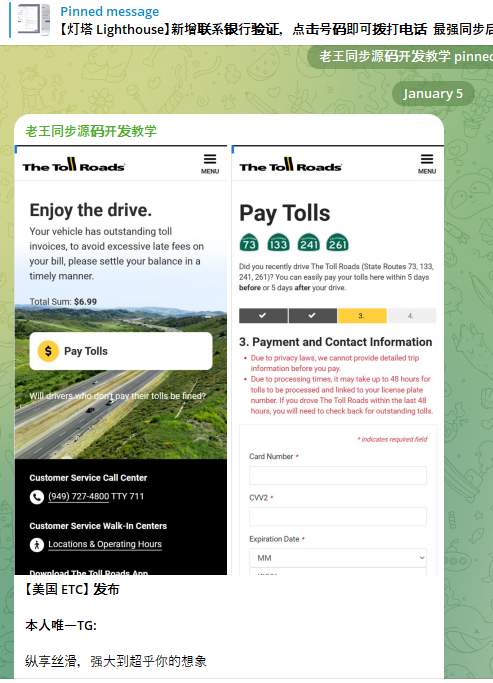
A component of the Chinese phishing kit Lighthouse made to target customers of The Toll Roads, which refers to several state routes through Orange County, Calif.
Lighthouse is one of several prolific phishing-as-a-service operations known as the “Smishing Triad,” and collectively they are responsible for sending millions of text messages that spoof the U.S. Postal Service to supposedly collect some outstanding delivery fee, or that pretend to be a local toll road operator warning of a delinquent toll fee. More recently, Lighthouse has been used to spoof e-commerce websites, financial institutions and brokerage firms.
Regardless of the text message lure used or brand used, the basic scam remains the same: After the visitor enters their payment information, the phishing site will automatically attempt to enroll the card as a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. The phishing site then tells the visitor that their bank is going to verify the transaction by sending a one-time code that needs to be entered into the payment page before the transaction can be completed.
If the recipient provides that one-time code, the scammers can link the victim’s card data to a mobile wallet on a device that they control. Researchers say the fraudsters usually load several stolen wallets onto each mobile device, and wait 7-10 days after that enrollment before selling the phones or using them for fraud.
Google called the scale of the Lighthouse phishing attacks “staggering.” A May 2025 report from Silent Push found the domains used by the Smishing Triad are rotated frequently, with approximately 25,000 phishing domains active during any 8-day period.
Google’s lawsuit alleges the purveyors of Lighthouse violated the company’s trademarks by including Google’s logos on countless phishing websites. The complaint says Lighthouse offers over 600 templates for phishing websites of more than 400 entities, and that Google’s logos were featured on at least a quarter of those templates.
Google is also pursuing Lighthouse under the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act, saying the Lighthouse phishing enterprise encompasses several connected threat actor groups that work together to design and implement complex criminal schemes targeting the general public.
According to Google, those threat actor teams include a “developer group” that supplies the phishing software and templates; a “data broker group” that provides a list of targets; a “spammer group” that provides the tools to send fraudulent text messages in volume; a “theft group,” in charge of monetizing the phished information; and an “administrative group,” which runs their Telegram support channels and discussion groups designed to facilitate collaboration and recruit new members.
“While different members of the Enterprise may play different roles in the Schemes, they all collaborate to execute phishing attacks that rely on the Lighthouse software,” Google’s complaint alleges. “None of the Enterprise’s Schemes can generate revenue without collaboration and cooperation among the members of the Enterprise. All of the threat actor groups are connected to one another through historical and current business ties, including through their use of Lighthouse and the online community supporting its use, which exists on both YouTube and Telegram channels.”
Silent Push’s May report observed that the Smishing Triad boasts it has “300+ front desk staff worldwide” involved in Lighthouse, staff that is mainly used to support various aspects of the group’s fraud and cash-out schemes.
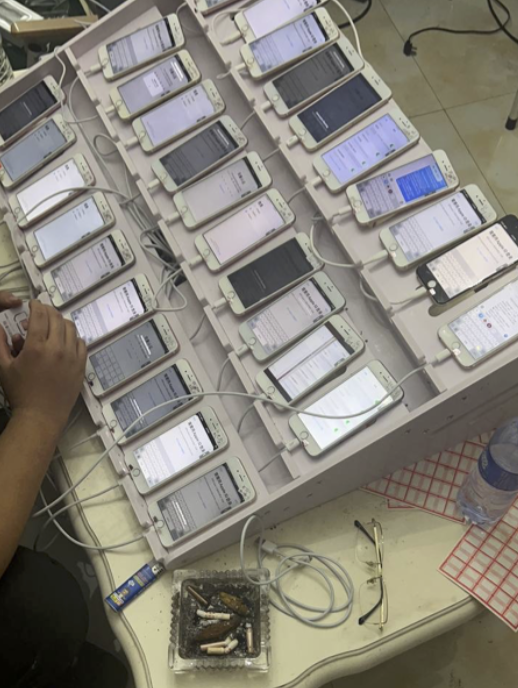

An image shared by an SMS phishing group shows a panel of mobile phones responsible for mass-sending phishing messages. These panels require a live operator because the one-time codes being shared by phishing victims must be used quickly as they generally expire within a few minutes.
Google alleges that in addition to blasting out text messages spoofing known brands, Lighthouse makes it easy for customers to mass-create fake e-commerce websites that are advertised using Google Ads accounts (and paid for with stolen credit cards). These phony merchants collect payment card information at checkout, and then prompt the customer to expect and share a one-time code sent from their financial institution.
Once again, that one-time code is being sent by the bank because the fake e-commerce site has just attempted to enroll the victim’s payment card data in a mobile wallet. By the time a victim understands they will likely never receive the item they just purchased from the fake e-commerce shop, the scammers have already run through hundreds of dollars in fraudulent charges, often at high-end electronics stores or jewelers.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company, and he’s been tracking Chinese SMS phishing groups for several years. Merrill said many Lighthouse customers are now using the phishing kit to erect fake e-commerce websites that are advertised on Google and Meta platforms.
“You find this shop by searching for a particular product online or whatever, and you think you’re getting a good deal,” Merrill said. “But of course you never receive the product, and they will phish that one-time code at checkout.”
Merrill said some of the phishing templates include payment buttons for services like PayPal, and that victims who choose to pay through PayPal can also see their PayPal accounts hijacked.

A fake e-commerce site from the Smishing Triad spoofing PayPal on a mobile device.
“The main advantage of the fake e-commerce site is that it doesn’t require them to send out message lures,” Merrill said, noting that the fake vendor sites have more staying power than traditional phishing sites because it takes far longer for them to be flagged for fraud.
Merrill said Google’s legal action may temporarily disrupt the Lighthouse operators, and could make it easier for U.S. federal authorities to bring criminal charges against the group. But he said the Chinese mobile phishing market is so lucrative right now that it’s difficult to imagine a popular phishing service voluntarily turning out the lights.
Merrill said Google’s lawsuit also can help lay the groundwork for future disruptive actions against Lighthouse and other phishing-as-a-service entities that are operating almost entirely on Chinese networks. According to Silent Push, a majority of the phishing sites created with these kits are sitting at two Chinese hosting companies: Tencent (AS132203) and Alibaba (AS45102).
“Once Google has a default judgment against the Lighthouse guys in court, theoretically they could use that to go to Alibaba and Tencent and say, ‘These guys have been found guilty, here are their domains and IP addresses, we want you to shut these down or we’ll include you in the case.'”
If Google can bring that kind of legal pressure consistently over time, Merrill said, they might succeed in increasing costs for the phishers and more frequently disrupting their operations.
“If you take all of these Chinese phishing kit developers, I have to believe it’s tens of thousands of Chinese-speaking people involved,” he said. “The Lighthouse guys will probably burn down their Telegram channels and disappear for a while. They might call it something else or redevelop their service entirely. But I don’t believe for a minute they’re going to close up shop and leave forever.”
Book Review: The Business of Secrets
The Business of Secrets: Adventures in Selling Encryption Around the World by Fred Kinch (May 24, 2004)
From the vantage point of today, it’s surreal reading about the commercial cryptography business in the 1970s. Nobody knew anything. The manufacturers didn’t know whether the cryptography they sold was any good. The customers didn’t know whether the crypto they bought was any good. Everyone pretended to know, thought they knew, or knew better than to even try to know.
The Business of Secrets is the self-published memoirs of Fred Kinch. He was founder and vice president of—mostly sales—at a US cryptographic hardware company called Datotek, from company’s founding in 1969 until 1982. It’s mostly a disjointed collection of stories about the difficulties of selling to governments worldwide, along with descriptions of the highs and (mostly) lows of foreign airlines, foreign hotels, and foreign travel in general. But it’s also about encryption...
Improving modern software supply chain security: From AI models to container images
On Hacking Back
Former DoJ attorney John Carlin writes about hackback, which he defines thus: “A hack back is a type of cyber response that incorporates a counterattack designed to proactively engage with, disable, or collect evidence about an attacker. Although hack backs can take on various forms, they are—by definition—not passive defensive measures.”
His conclusion:
As the law currently stands, specific forms of purely defense measures are authorized so long as they affect only the victim’s system or data.
At the other end of the spectrum, offensive measures that involve accessing or otherwise causing damage or loss to the hacker’s systems are likely prohibited, absent government oversight or authorization. And even then parties should proceed with caution in light of the heightened risks of misattribution, collateral damage, and retaliation...
Prepare for a post-quantum future with RHEL 9.7
Prompt Injection in AI Browsers
This is why AIs are not ready to be personal assistants:
A new attack called ‘CometJacking’ exploits URL parameters to pass to Perplexity’s Comet AI browser hidden instructions that allow access to sensitive data from connected services, like email and calendar.
In a realistic scenario, no credentials or user interaction are required and a threat actor can leverage the attack by simply exposing a maliciously crafted URL to targeted users.
[…]
CometJacking is a prompt-injection attack where the query string processed by the Comet AI browser contains malicious instructions added using the ‘collection’ parameter of the URL...
A deeper look at post-quantum cryptography support in Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 control plane
New Attacks Against Secure Enclaves
Encryption can protect data at rest and data in transit, but does nothing for data in use. What we have are secure enclaves. I’ve written about this before:
Almost all cloud services have to perform some computation on our data. Even the simplest storage provider has code to copy bytes from an internal storage system and deliver them to the user. End-to-end encryption is sufficient in such a narrow context. But often we want our cloud providers to be able to perform computation on our raw data: search, analysis, AI model training or fine-tuning, and more. Without expensive, esoteric techniques, such as secure multiparty computation protocols or homomorphic encryption techniques that can perform calculations on encrypted data, cloud servers require access to the unencrypted data to do anything useful...
The New 2025 OWASP Top 10 List: What Changed, and What You Need to Know
Drilling Down on Uncle Sam’s Proposed TP-Link Ban
The U.S. government is reportedly preparing to ban the sale of wireless routers and other networking gear from TP-Link Systems, a tech company that currently enjoys an estimated 50% market share among home users and small businesses. Experts say while the proposed ban may have more to do with TP-Link’s ties to China than any specific technical threats, much of the rest of the industry serving this market also sources hardware from China and ships products that are insecure fresh out of the box.

A TP-Link WiFi 6 AX1800 Smart WiFi Router (Archer AX20).
The Washington Post recently reported that more than a half-dozen federal departments and agencies were backing a proposed ban on future sales of TP-Link devices in the United States. The story said U.S. Department of Commerce officials concluded TP-Link Systems products pose a risk because the U.S.-based company’s products handle sensitive American data and because the officials believe it remains subject to jurisdiction or influence by the Chinese government.
TP-Link Systems denies that, saying that it fully split from the Chinese TP-Link Technologies over the past three years, and that its critics have vastly overstated the company’s market share (TP-Link puts it at around 30 percent). TP-Link says it has headquarters in California, with a branch in Singapore, and that it manufactures in Vietnam. The company says it researches, designs, develops and manufactures everything except its chipsets in-house.
TP-Link Systems told The Post it has sole ownership of some engineering, design and manufacturing capabilities in China that were once part of China-based TP-Link Technologies, and that it operates them without Chinese government supervision.
“TP-Link vigorously disputes any allegation that its products present national security risks to the United States,” Ricca Silverio, a spokeswoman for TP-Link Systems, said in a statement. “TP-Link is a U.S. company committed to supplying high-quality and secure products to the U.S. market and beyond.”
Cost is a big reason TP-Link devices are so prevalent in the consumer and small business market: As this February 2025 story from Wired observed regarding the proposed ban, TP-Link has long had a reputation for flooding the market with devices that are considerably cheaper than comparable models from other vendors. That price point (and consistently excellent performance ratings) has made TP-Link a favorite among Internet service providers (ISPs) that provide routers to their customers.
In August 2024, the chairman and the ranking member of the House Select Committee on the Strategic Competition Between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party called for an investigation into TP-Link devices, which they said were found on U.S. military bases and for sale at exchanges that sell them to members of the military and their families.
“TP-Link’s unusual degree of vulnerabilities and required compliance with PRC law are in and of themselves disconcerting,” the House lawmakers warned in a letter (PDF) to the director of the Commerce Department. “When combined with the PRC government’s common use of SOHO [small office/home office] routers like TP-Link to perpetrate extensive cyberattacks in the United States, it becomes significantly alarming.”
The letter cited a May 2023 blog post by Check Point Research about a Chinese state-sponsored hacking group dubbed “Camaro Dragon” that used a malicious firmware implant for some TP-Link routers to carry out a sequence of targeted cyberattacks against European foreign affairs entities. Check Point said while it only found the malicious firmware on TP-Link devices, “the firmware-agnostic nature of the implanted components indicates that a wide range of devices and vendors may be at risk.”
In a report published in October 2024, Microsoft said it was tracking a network of compromised TP-Link small office and home office routers that has been abused by multiple distinct Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups since 2021. Microsoft found the hacker groups were leveraging the compromised TP-Link systems to conduct “password spraying” attacks against Microsoft accounts. Password spraying involves rapidly attempting to access a large number of accounts (usernames/email addresses) with a relatively small number of commonly used passwords.
TP-Link rightly points out that most of its competitors likewise source components from China. The company also correctly notes that advanced persistent threat (APT) groups from China and other nations have leveraged vulnerabilities in products from their competitors, such as Cisco and Netgear.
But that may be cold comfort for TP-Link customers who are now wondering if it’s smart to continue using these products, or whether it makes sense to buy more costly networking gear that might only be marginally less vulnerable to compromise.
Almost without exception, the hardware and software that ships with most consumer-grade routers includes a number of default settings that need to be changed before the devices can be safely connected to the Internet. For example, bring a new router online without changing the default username and password and chances are it will only take a few minutes before it is probed and possibly compromised by some type of Internet-of-Things botnet. Also, it is incredibly common for the firmware in a brand new router to be dangerously out of date by the time it is purchased and unboxed.
Until quite recently, the idea that router manufacturers should make it easier for their customers to use these products safely was something of anathema to this industry. Consumers were largely left to figure that out on their own, with predictably disastrous results.
But over the past few years, many manufacturers of popular consumer routers have begun forcing users to perform basic hygiene — such as changing the default password and updating the internal firmware — before the devices can be used as a router. For example, most brands of “mesh” wireless routers — like Amazon’s Eero, Netgear’s Orbi series, or Asus’s ZenWifi — require online registration that automates these critical steps going forward (or at least through their stated support lifecycle).
For better or worse, less expensive, traditional consumer routers like those from Belkin and Linksys also now automate this setup by heavily steering customers toward installing a mobile app to complete the installation (this often comes as a shock to people more accustomed to manually configuring a router). Still, these products tend to put the onus on users to check for and install available updates periodically. Also, they’re often powered by underwhelming or else bloated firmware, and a dearth of configurable options.
Of course, not everyone wants to fiddle with mobile apps or is comfortable with registering their router so that it can be managed or monitored remotely in the cloud. For those hands-on folks — and for power users seeking more advanced router features like VPNs, ad blockers and network monitoring — the best advice is to check if your router’s stock firmware can be replaced with open-source alternatives, such as OpenWrt or DD-WRT.
These open-source firmware options are compatible with a wide range of devices, and they generally offer more features and configurability. Open-source firmware can even help extend the life of routers years after the vendor stops supporting the underlying hardware, but it still requires users to manually check for and install any available updates.
Happily, TP-Link users spooked by the proposed ban may have an alternative to outright junking these devices, as many TP-Link routers also support open-source firmware options like OpenWRT. While this approach may not eliminate any potential hardware-specific security flaws, it could serve as an effective hedge against more common vendor-specific vulnerabilities, such as undocumented user accounts, hard-coded credentials, and weaknesses that allow attackers to bypass authentication.
Regardless of the brand, if your router is more than four or five years old it may be worth upgrading for performance reasons alone — particularly if your home or office is primarily accessing the Internet through WiFi.
NB: The Post’s story notes that a substantial portion of TP-Link routers and those of its competitors are purchased or leased through ISPs. In these cases, the devices are typically managed and updated remotely by your ISP, and equipped with custom profiles responsible for authenticating your device to the ISP’s network. If this describes your setup, please do not attempt to modify or replace these devices without first consulting with your Internet provider.
Friday Squid Blogging: Squid Game: The Challenge, Season Two
The second season of the Netflix reality competition show Squid Game: The Challenge has dropped. (Too many links to pick a few—search for it.)
As usual, you can also use this squid post to talk about the security stories in the news that I haven’t covered.
Faking Receipts with AI
Over the past few decades, it’s become easier and easier to create fake receipts. Decades ago, it required special paper and printers—I remember a company in the UK advertising its services to people trying to cover up their affairs. Then, receipts became computerized, and faking them required some artistic skills to make the page look realistic.
Now, AI can do it all:
Several receipts shown to the FT by expense management platforms demonstrated the realistic nature of the images, which included wrinkles in paper, detailed itemization that matched real-life menus, and signatures...
Rigged Poker Games
The Department of Justice has indicted thirty-one people over the high-tech rigging of high-stakes poker games.
In a typical legitimate poker game, a dealer uses a shuffling machine to shuffle the cards randomly before dealing them to all the players in a particular order. As set forth in the indictment, the rigged games used altered shuffling machines that contained hidden technology allowing the machines to read all the cards in the deck. Because the cards were always dealt in a particular order to the players at the table, the machines could determine which player would have the winning hand. This information was transmitted to an off-site member of the conspiracy, who then transmitted that information via cellphone back to a member of the conspiracy who was playing at the table, referred to as the “Quarterback” or “Driver.” The Quarterback then secretly signaled this information (usually by prearranged signals like touching certain chips or other items on the table) to other co-conspirators playing at the table, who were also participants in the scheme. Collectively, the Quarterback and other players in on the scheme (i.e., the cheating team) used this information to win poker games against unwitting victims, who sometimes lost tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars at a time. The defendants used other cheating technology as well, such as a chip tray analyzer (essentially, a poker chip tray that also secretly read all cards using hidden cameras), an x-ray table that could read cards face down on the table, and special contact lenses or eyeglasses that could read pre-marked cards. ...