Software Security
Most Parked Domains Now Serving Malicious Content
Direct navigation — the act of visiting a website by manually typing a domain name in a web browser — has never been riskier: A new study finds the vast majority of “parked” domains — mostly expired or dormant domain names, or common misspellings of popular websites — are now configured to redirect visitors to sites that foist scams and malware.
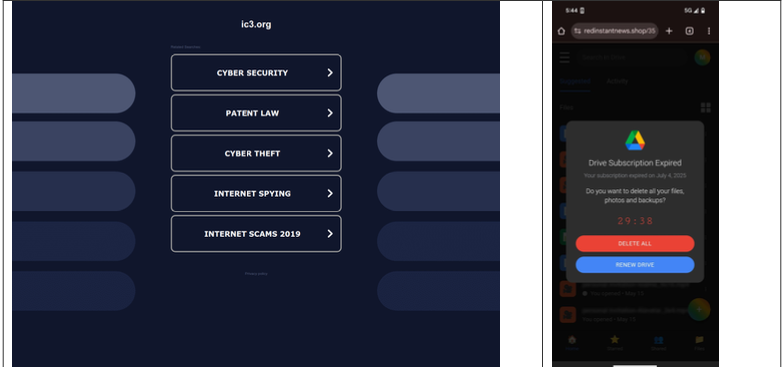
A lookalike domain to the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center website, returned a non-threatening parking page (left) whereas a mobile user was instantly directed to deceptive content in October 2025 (right). Image: Infoblox.
When Internet users try to visit expired domain names or accidentally navigate to a lookalike “typosquatting” domain, they are typically brought to a placeholder page at a domain parking company that tries to monetize the wayward traffic by displaying links to a number of third-party websites that have paid to have their links shown.
A decade ago, ending up at one of these parked domains came with a relatively small chance of being redirected to a malicious destination: In 2014, researchers found (PDF) that parked domains redirected users to malicious sites less than five percent of the time — regardless of whether the visitor clicked on any links at the parked page.
But in a series of experiments over the past few months, researchers at the security firm Infoblox say they discovered the situation is now reversed, and that malicious content is by far the norm now for parked websites.
“In large scale experiments, we found that over 90% of the time, visitors to a parked domain would be directed to illegal content, scams, scareware and anti-virus software subscriptions, or malware, as the ‘click’ was sold from the parking company to advertisers, who often resold that traffic to yet another party,” Infoblox researchers wrote in a paper published today.
Infoblox found parked websites are benign if the visitor arrives at the site using a virtual private network (VPN), or else via a non-residential Internet address. For example, Scotiabank.com customers who accidentally mistype the domain as scotaibank[.]com will see a normal parking page if they’re using a VPN, but will be redirected to a site that tries to foist scams, malware or other unwanted content if coming from a residential IP address. Again, this redirect happens just by visiting the misspelled domain with a mobile device or desktop computer that is using a residential IP address.
According to Infoblox, the person or entity that owns scotaibank[.]com has a portfolio of nearly 3,000 lookalike domains, including gmai[.]com, which demonstrably has been configured with its own mail server for accepting incoming email messages. Meaning, if you send an email to a Gmail user and accidentally omit the “l” from “gmail.com,” that missive doesn’t just disappear into the ether or produce a bounce reply: It goes straight to these scammers. The report notices this domain also has been leveraged in multiple recent business email compromise campaigns, using a lure indicating a failed payment with trojan malware attached.
Infoblox found this particular domain holder (betrayed by a common DNS server — torresdns[.]com) has set up typosquatting domains targeting dozens of top Internet destinations, including Craigslist, YouTube, Google, Wikipedia, Netflix, TripAdvisor, Yahoo, eBay, and Microsoft. A defanged list of these typosquatting domains is available here (the dots in the listed domains have been replaced with commas).
David Brunsdon, a threat researcher at Infoblox, said the parked pages send visitors through a chain of redirects, all while profiling the visitor’s system using IP geolocation, device fingerprinting, and cookies to determine where to redirect domain visitors.
“It was often a chain of redirects — one or two domains outside the parking company — before threat arrives,” Brunsdon said. “Each time in the handoff the device is profiled again and again, before being passed off to a malicious domain or else a decoy page like Amazon.com or Alibaba.com if they decide it’s not worth targeting.”
Brunsdon said domain parking services claim the search results they return on parked pages are designed to be relevant to their parked domains, but that almost none of this displayed content was related to the lookalike domain names they tested.
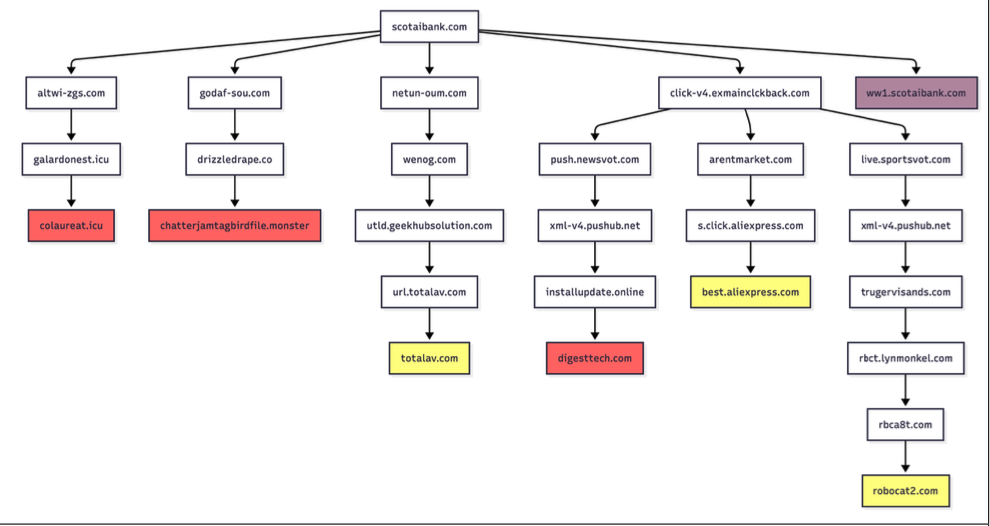
Samples of redirection paths when visiting scotaibank dot com. Each branch includes a series of domains observed, including the color-coded landing page. Image: Infoblox.
Infoblox said a different threat actor who owns domaincntrol[.]com — a domain that differs from GoDaddy’s name servers by a single character — has long taken advantage of typos in DNS configurations to drive users to malicious websites. In recent months, however, Infoblox discovered the malicious redirect only happens when the query for the misconfigured domain comes from a visitor who is using Cloudflare’s DNS resolvers (1.1.1.1), and that all other visitors will get a page that refuses to load.
The researchers found that even variations on well-known government domains are being targeted by malicious ad networks.
“When one of our researchers tried to report a crime to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), they accidentally visited ic3[.]org instead of ic3[.]gov,” the report notes. “Their phone was quickly redirected to a false ‘Drive Subscription Expired’ page. They were lucky to receive a scam; based on what we’ve learnt, they could just as easily receive an information stealer or trojan malware.”
The Infoblox report emphasizes that the malicious activity they tracked is not attributed to any known party, noting that the domain parking or advertising platforms named in the study were not implicated in the malvertising they documented.
However, the report concludes that while the parking companies claim to only work with top advertisers, the traffic to these domains was frequently sold to affiliate networks, who often resold the traffic to the point where the final advertiser had no business relationship with the parking companies.
Infoblox also pointed out that recent policy changes by Google may have inadvertently increased the risk to users from direct search abuse. Brunsdon said Google Adsense previously defaulted to allowing their ads to be placed on parked pages, but that in early 2025 Google implemented a default setting that had their customers opt-out by default on presenting ads on parked domains — requiring the person running the ad to voluntarily go into their settings and turn on parking as a location.
Chinese Surveillance and AI
New report: “The Party’s AI: How China’s New AI Systems are Reshaping Human Rights.” From a summary article:
China is already the world’s largest exporter of AI powered surveillance technology; new surveillance technologies and platforms developed in China are also not likely to simply stay there. By exposing the full scope of China’s AI driven control apparatus, this report presents clear, evidence based insights for policymakers, civil society, the media and technology companies seeking to counter the rise of AI enabled repression and human rights violations, and China’s growing efforts to project that repression beyond its borders...
Red Hat to acquire Chatterbox Labs: Frequently Asked Questions
Accelerating NetOps transformation with Ansible Automation Platform
Against the Federal Moratorium on State-Level Regulation of AI
Cast your mind back to May of this year: Congress was in the throes of debate over the massive budget bill. Amidst the many seismic provisions, Senator Ted Cruz dropped a ticking time bomb of tech policy: a ten-year moratorium on the ability of states to regulate artificial intelligence. To many, this was catastrophic. The few massive AI companies seem to be swallowing our economy whole: their energy demands are overriding household needs, their data demands are overriding creators’ copyright, and their products are triggering mass unemployment as well as new types of clinical ...
Harden your AI systems: Applying industry standards in the real world
Upcoming Speaking Engagements
This is a current list of where and when I am scheduled to speak:
- I’m speaking and signing books at the Chicago Public Library in Chicago, Illinois, USA, at 6:00 PM CT on February 5, 2026. Details to come.
- I’m speaking at Capricon 44 in Chicago, Illinois, USA. The convention runs February 5-8, 2026. My speaking time is TBD.
- I’m speaking at the Munich Cybersecurity Conference in Munich, Germany on February 12, 2026.
- I’m speaking at Tech Live: Cybersecurity in New York City, USA on March 11, 2026.
- I’m giving the Ross Anderson Lecture at the University of Cambridge’s Churchill College on March 19, 2026...
Friday Squid Blogging: Giant Squid Eating a Diamondback Squid
I have no context for this video—it’s from Reddit—but one of the commenters adds some context:
Hey everyone, squid biologist here! Wanted to add some stuff you might find interesting.
With so many people carrying around cameras, we’re getting more videos of giant squid at the surface than in previous decades. We’re also starting to notice a pattern, that around this time of year (peaking in January) we see a bunch of giant squid around Japan. We don’t know why this is happening. Maybe they gather around there to mate or something? who knows! but since so many people have cameras, those one-off monster-story encounters are now caught on video, like this one (which, btw, rips. This squid looks so healthy, it’s awesome)...
Building Trustworthy AI Agents
The promise of personal AI assistants rests on a dangerous assumption: that we can trust systems we haven’t made trustworthy. We can’t. And today’s versions are failing us in predictable ways: pushing us to do things against our own best interests, gaslighting us with doubt about things we are or that we know, and being unable to distinguish between who we are and who we have been. They struggle with incomplete, inaccurate, and partial context: with no standard way to move toward accuracy, no mechanism to correct sources of error, and no accountability when wrong information leads to bad decisions...
AIs Exploiting Smart Contracts
I have long maintained that smart contracts are a dumb idea: that a human process is actually a security feature.
Here’s some interesting research on training AIs to automatically exploit smart contracts:
AI models are increasingly good at cyber tasks, as we’ve written about before. But what is the economic impact of these capabilities? In a recent MATS and Anthropic Fellows project, our scholars investigated this question by evaluating AI agents’ ability to exploit smart contracts on Smart CONtracts Exploitation benchmark (SCONE-bench)a new benchmark they built comprising 405 contracts that were actually exploited between 2020 and 2025. On contracts exploited after the latest knowledge cutoffs (June 2025 for Opus 4.5 and March 2025 for other models), Claude Opus 4.5, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and GPT-5 developed exploits collectively worth $4.6 million, establishing a concrete lower bound for the economic harm these capabilities could enable. Going beyond retrospective analysis, we evaluated both Sonnet 4.5 and GPT-5 in simulation against 2,849 recently deployed contracts without any known vulnerabilities. Both agents uncovered two novel zero-day vulnerabilities and produced exploits worth $3,694, with GPT-5 doing so at an API cost of $3,476. This demonstrates as a proof-of-concept that profitable, real-world autonomous exploitation is technically feasible, a finding that underscores the need for proactive adoption of AI for defense...
Introducing the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant
From incident responder to security steward: My journey to understanding Red Hat's open approach to vulnerability management
The Sleep Test: How Embracing Chaos Unlocks API Resilience
React2Shell Continued: What to know and do about the 2 latest CVEs
FBI Warns of Fake Video Scams
The FBI is warning of AI-assisted fake kidnapping scams:
Criminal actors typically will contact their victims through text message claiming they have kidnapped their loved one and demand a ransom be paid for their release. Oftentimes, the criminal actor will express significant claims of violence towards the loved one if the ransom is not paid immediately. The criminal actor will then send what appears to be a genuine photo or video of the victim’s loved one, which upon close inspection often reveals inaccuracies when compared to confirmed photos of the loved one. Examples of these inaccuracies include missing tattoos or scars and inaccurate body proportions. Criminal actors will sometimes purposefully send these photos using timed message features to limit the amount of time victims have to analyze the images...
Slash VM provisioning time on Red Hat Openshift Virtualization using Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
DDoS in November
Microsoft Patch Tuesday, December 2025 Edition
Microsoft today pushed updates to fix at least 56 security flaws in its Windows operating systems and supported software. This final Patch Tuesday of 2025 tackles one zero-day bug that is already being exploited, as well as two publicly disclosed vulnerabilities.

Despite releasing a lower-than-normal number of security updates these past few months, Microsoft patched a whopping 1,129 vulnerabilities in 2025, an 11.9% increase from 2024. According to Satnam Narang at Tenable, this year marks the second consecutive year that Microsoft patched over one thousand vulnerabilities, and the third time it has done so since its inception.
The zero-day flaw patched today is CVE-2025-62221, a privilege escalation vulnerability affecting Windows 10 and later editions. The weakness resides in a component called the “Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver” — a system driver that enables cloud applications to access file system functionalities.
“This is particularly concerning, as the mini filter is integral to services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and iCloud, and remains a core Windows component, even if none of those apps were installed,” said Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7.
Only three of the flaws patched today earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating: Both CVE-2025-62554 and CVE-2025-62557 involve Microsoft Office, and both can exploited merely by viewing a booby-trapped email message in the Preview Pane. Another critical bug — CVE-2025-62562 — involves Microsoft Outlook, although Redmond says the Preview Pane is not an attack vector with this one.
But according to Microsoft, the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited from this month’s patch batch are other (non-critical) privilege escalation bugs, including:
–CVE-2025-62458 — Win32k
–CVE-2025-62470 — Windows Common Log File System Driver
–CVE-2025-62472 — Windows Remote Access Connection Manager
–CVE-2025-59516 — Windows Storage VSP Driver
–CVE-2025-59517 — Windows Storage VSP Driver
Kev Breen, senior director of threat research at Immersive, said privilege escalation flaws are observed in almost every incident involving host compromises.
“We don’t know why Microsoft has marked these specifically as more likely, but the majority of these components have historically been exploited in the wild or have enough technical detail on previous CVEs that it would be easier for threat actors to weaponize these,” Breen said. “Either way, while not actively being exploited, these should be patched sooner rather than later.”
One of the more interesting vulnerabilities patched this month is CVE-2025-64671, a remote code execution flaw in the Github Copilot Plugin for Jetbrains AI-based coding assistant that is used by Microsoft and GitHub. Breen said this flaw would allow attackers to execute arbitrary code by tricking the large language model (LLM) into running commands that bypass the guardrails and add malicious instructions in the user’s “auto-approve” settings.
CVE-2025-64671 is part of a broader, more systemic security crisis that security researcher Ari Marzuk has branded IDEsaster (IDE stands for “integrated development environment”), which encompasses more than 30 separate vulnerabilities reported in nearly a dozen market-leading AI coding platforms, including Cursor, Windsurf, Gemini CLI, and Claude Code.
The other publicly-disclosed vulnerability patched today is CVE-2025-54100, a remote code execution bug in Windows Powershell on Windows Server 2008 and later that allows an unauthenticated attacker to run code in the security context of the user.
For anyone seeking a more granular breakdown of the security updates Microsoft pushed today, check out the roundup at the SANS Internet Storm Center. As always, please leave a note in the comments if you experience problems applying any of this month’s Windows patches.
AI vs. Human Drivers
Two competing arguments are making the rounds. The first is by a neurosurgeon in the New York Times. In an op-ed that honestly sounds like it was paid for by Waymo, the author calls driverless cars a “public health breakthrough”:
In medical research, there’s a practice of ending a study early when the results are too striking to ignore. We stop when there is unexpected harm. We also stop for overwhelming benefit, when a treatment is working so well that it would be unethical to continue giving anyone a placebo. When an intervention works this clearly, you change what you do...